Carboxylic Acid To Aldehyde Mechanism
Alcohols can be prepared from carbonyl compounds such as aldehydes ketones esters acid chlorides and even carboxylic acids by hydride reductions. The most fruitful approach to this end has been to attach alkoxy or alkyl groups on the aluminum.
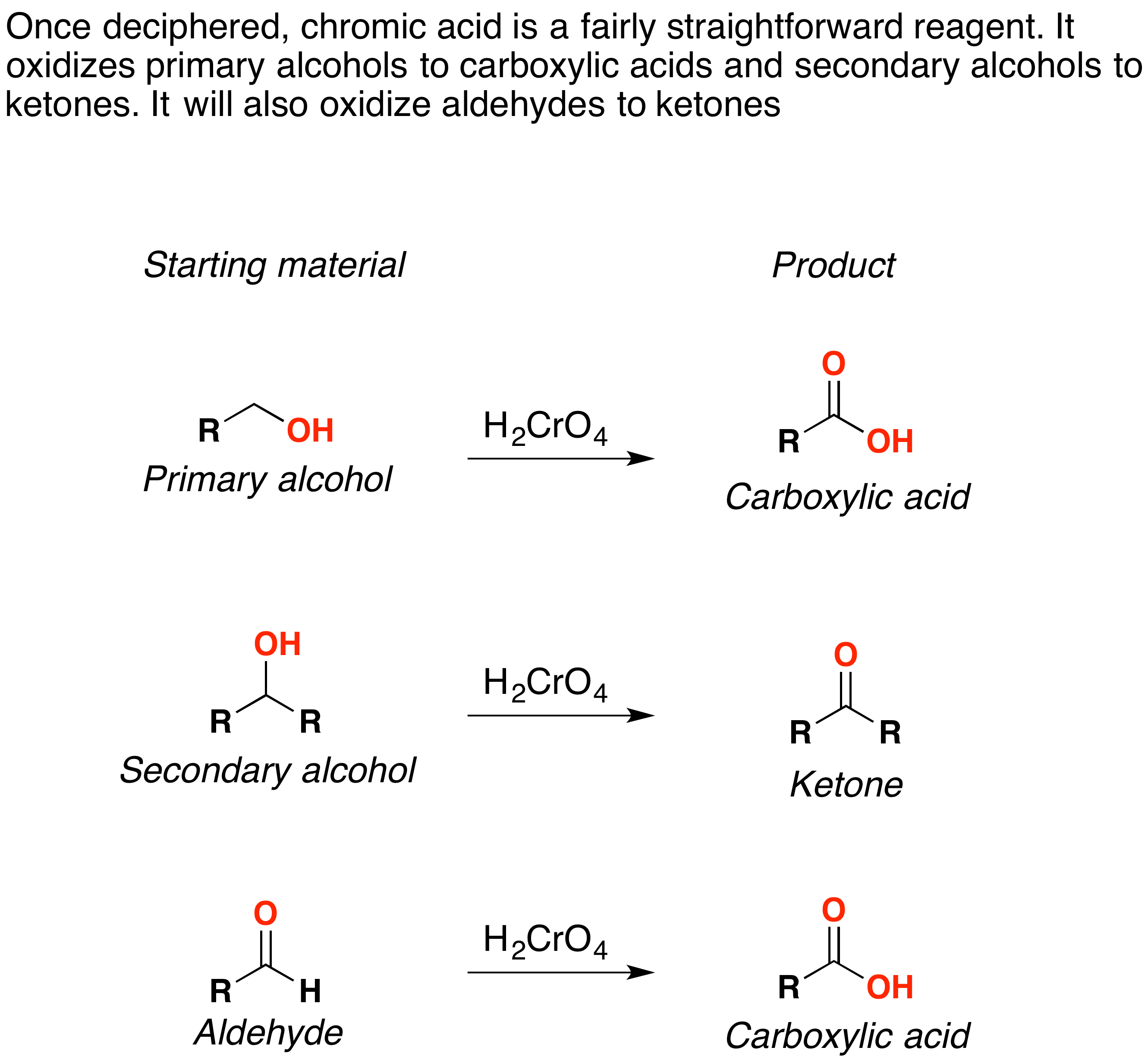
Primary alcohol is oxidized to carboxylic acid by h kmno 4 or h k 2 cro 4 or h k 2 cr 2 o 7.
Carboxylic acid to aldehyde mechanism. The carboxyl carbon of the carboxylic acid is protonated. But aldehyde is again oxidized to carboxylic acid. So aldehyde cannot be separated.
Because lithium tetrahydridoaluminate reacts rapidly with aldehydes it is impossible to stop at the halfway stage. Since relatively few methods exist for the reduction of carboxylic acid derivatives to aldehydes it would be useful to modify the reactivity and solubility of lah to permit partial reductions of this kind to be achieved. In this mechanism an alcohol is added to a carboxylic acid by the following steps.
The most common hydride reducing agents are the lithium aluminum hydride lialh4 also abbreviated as lah and sodium borohydride nabh4. The product formed in the reaction will show resonance. Generally we use weak acids as catalysts in the addition reaction of aldehydes and ketones with ammonia and its derivatives.
The fischer esterification proceeds via a carbocation mechanism. Oxidation of aldehydes to carboxylic acids. Refer to the example below.
In the first step one mol of water is added in the presence of an acidic catalyst to generate a hydrate geminal 1 1 diol. As an intermediate product aldehyde is given. The oxidation of aldehydes to carboxylic acids is a two step procedure.
Carboxylic acid derivatives aldehydes and ketones to alcohols hydride reduction mechanism. Lialh4 and nabh4 carbonyl reduction mechanism. Full oxidation to carboxylic acids.
Primary alcohols can be oxidized to either aldehydes or carboxylic acids depending on the reaction conditions. These reductions are a result of a net addition of two hydrogen atoms to the c o bond. The reaction mechanism for metal hydride reduction is based on nucleophilic addition of hydride to the carbonyl carbon.
So we cannot produce an aldehyde from the reaction of primary alcohols and strong oxidizing agents. In the case of the formation of carboxylic acids the alcohol is first oxidized to an aldehyde which is then oxidized further to the acid. In some cases the alkali metal cation especially li activates the carbonyl group by coordinating to the carbonyl oxygen thereby enhancing the electrophilicity of the carbonyl.
Equations for these reactions are usually written in a simplified form for uk a level purposes. The reduction of a carboxylic acid the reaction happens in two stages first to form an aldehyde and then a primary alcohol. Similar to aldehydes and ketones carboxylic acids can be halogenated at the alpha α carbon by treatment with a halogen cl 2 or br 2 and a catalyst usually phosphorus trichloride pcl 3.
The carbonyl group in aldehydes or ketone contains lone pair which reacts with weak acids. This reaction called the hell volhard zelinskii reaction actually takes place on the acyl halide rather than on the acid itself.
 Oxidation Of Alcohols Mechanisms And Practice Problems In 2020
Oxidation Of Alcohols Mechanisms And Practice Problems In 2020
 Oxidation By Chromic Acid Chemistry Libretexts
Oxidation By Chromic Acid Chemistry Libretexts
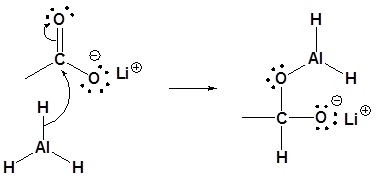 20 7 Reduction Of Carboxylic Acids And Their Derivatives
20 7 Reduction Of Carboxylic Acids And Their Derivatives
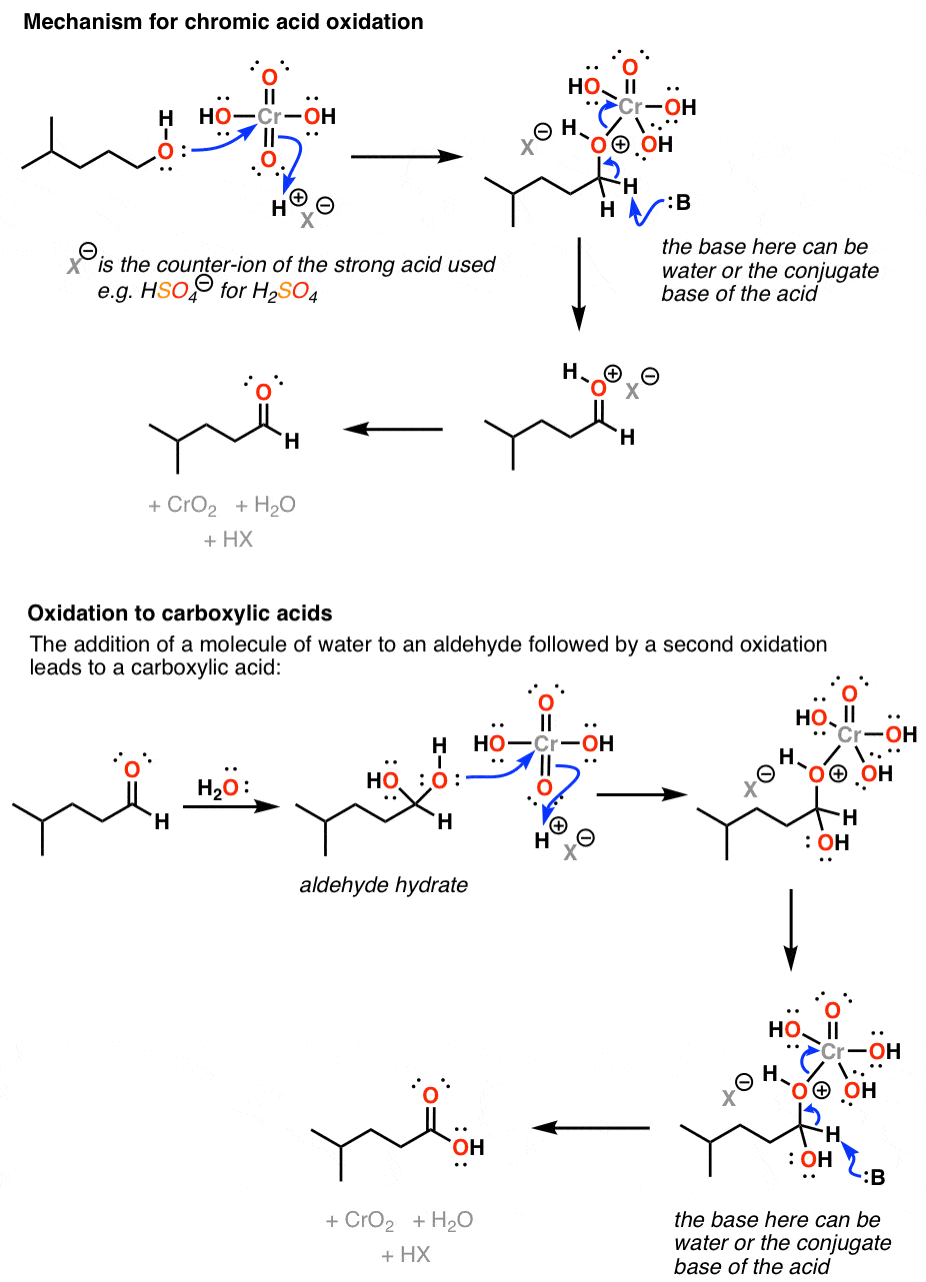 Reagent Friday Chromic Acid H2cro4 Master Organic Chemistry
Reagent Friday Chromic Acid H2cro4 Master Organic Chemistry
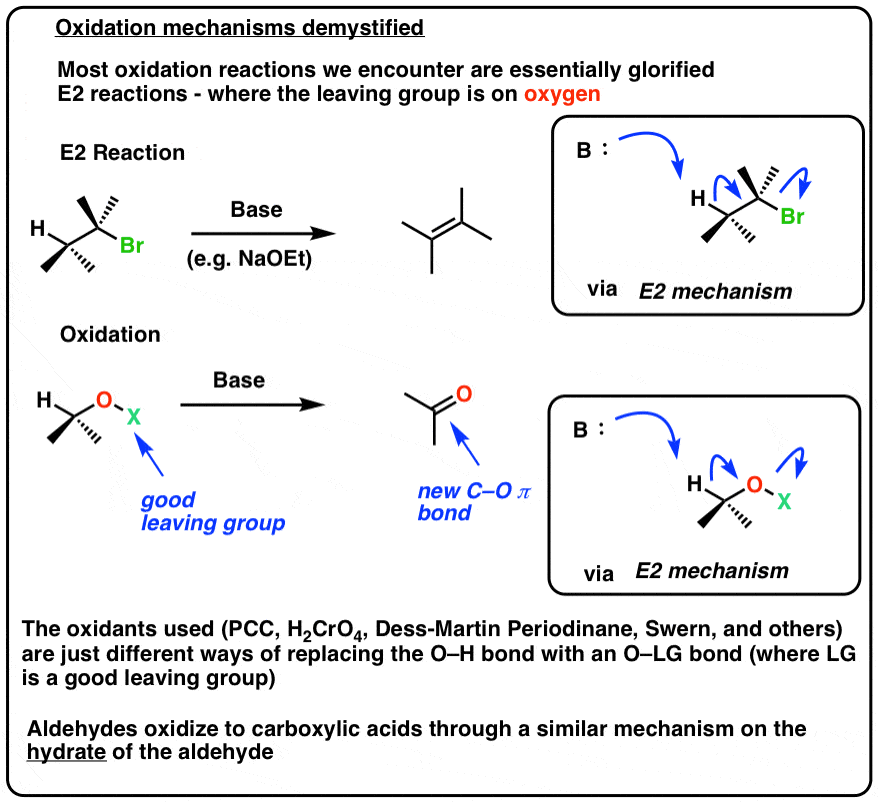 Demystifying The Mechanism For Oxidation Of Alcohols And Aldehydes
Demystifying The Mechanism For Oxidation Of Alcohols And Aldehydes
Oxidation Of Aldehydes To Carboxylic Acids Chemgapedia
 Oxidation To Carboxylic Acid H2cro4 Or Kmno4 Chemistryscore
Oxidation To Carboxylic Acid H2cro4 Or Kmno4 Chemistryscore
 Oxidation To Carboxylic Acids Tollens Chemistryscore
Oxidation To Carboxylic Acids Tollens Chemistryscore
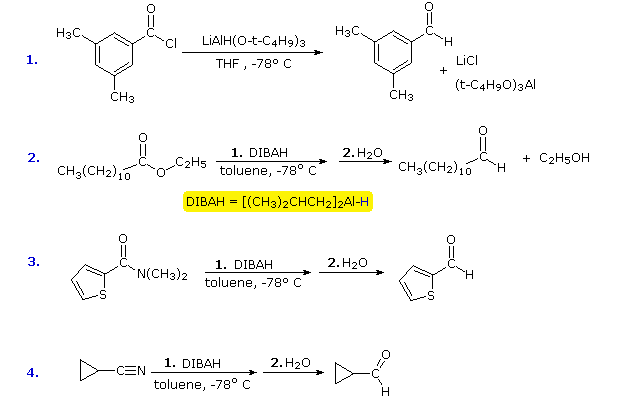 Carboxyl Derivative Reactivity
Carboxyl Derivative Reactivity
 Dependence Of Primary Alcohol Oxidation On Presence Of Water And
Dependence Of Primary Alcohol Oxidation On Presence Of Water And
Oxidation Of Aldehydes To Carboxylic Acids Chemgapedia
Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gcqqnrrypmcaitpoq6xud Wlbdviq 5bw80ho9378 Mzxw4jdgqt Usqp Cau
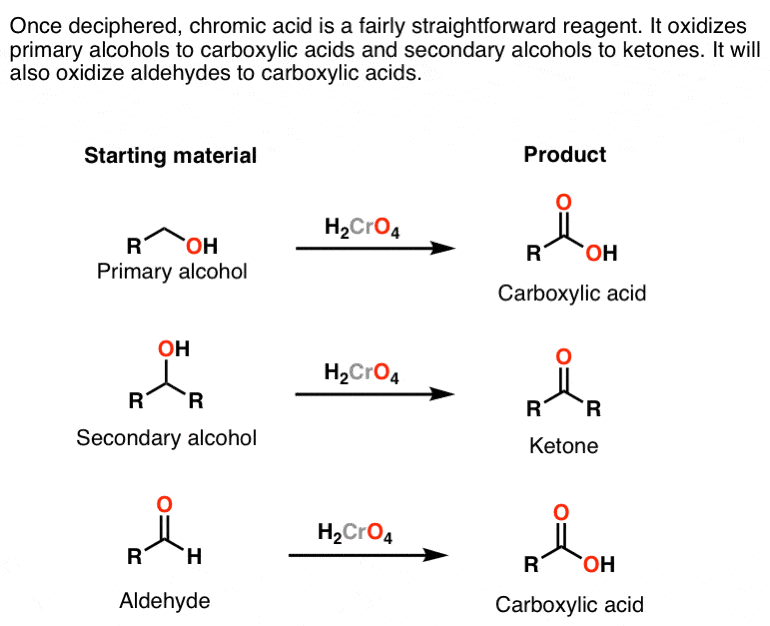 Reagent Friday Chromic Acid H2cro4 Master Organic Chemistry
Reagent Friday Chromic Acid H2cro4 Master Organic Chemistry
 Reaction Of An Aldehyde With Cysteine Can Result Among Others In
Reaction Of An Aldehyde With Cysteine Can Result Among Others In
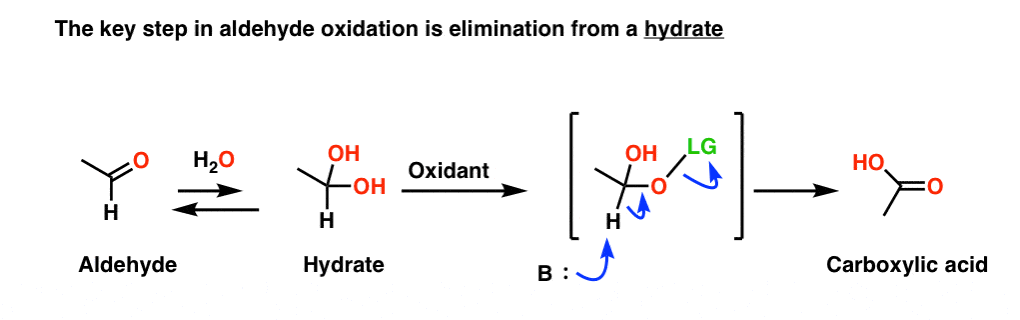 Demystifying The Mechanism For Oxidation Of Alcohols And Aldehydes
Demystifying The Mechanism For Oxidation Of Alcohols And Aldehydes
Oxidation Of Aldehydes To Carboxylic Acids Chemgapedia
 Reactions Of Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic Acids Mcat Organic
Reactions Of Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic Acids Mcat Organic
Reactions Of Carboxylic Acids Chemgapedia
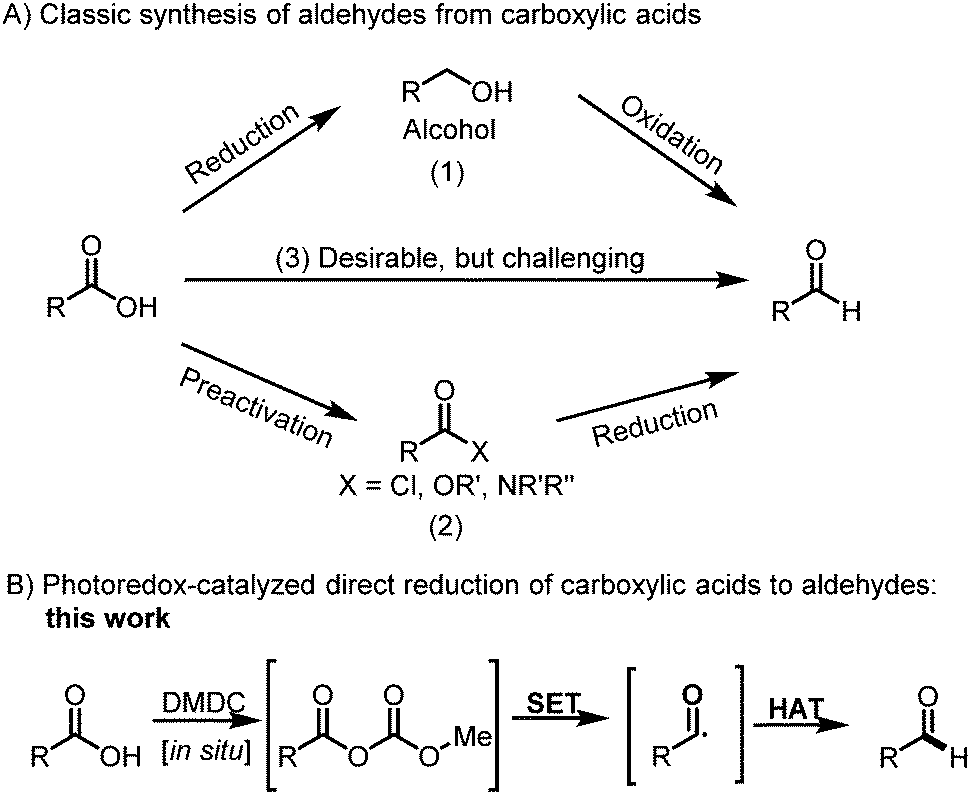 Selective Reduction Of Carboxylic Acids To Aldehydes With
Selective Reduction Of Carboxylic Acids To Aldehydes With
 Oxidation Of Aldehydes And Ketones To Carboxylic Acids After
Oxidation Of Aldehydes And Ketones To Carboxylic Acids After

 Nitrile Reduction Mechanism With Lialh4 And Dibal To Amine Or
Nitrile Reduction Mechanism With Lialh4 And Dibal To Amine Or
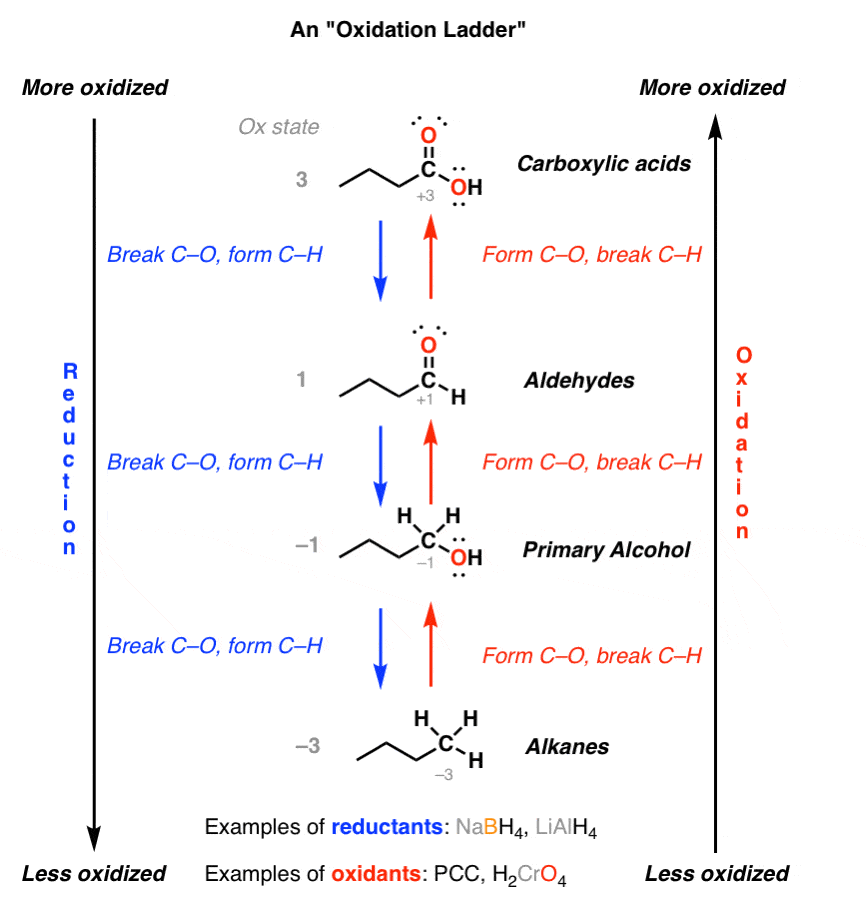 Oxidation Ladders Master Organic Chemistry
Oxidation Ladders Master Organic Chemistry
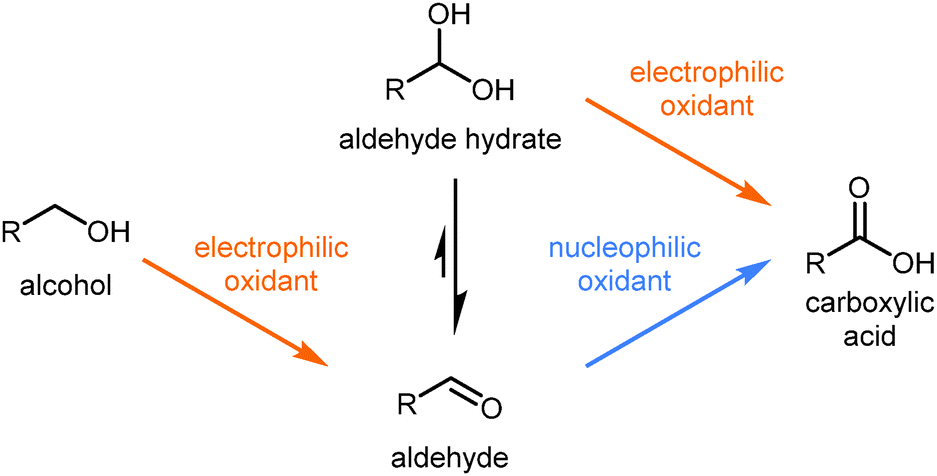 Oxidation Of Allylic And Benzylic Alcohols To Aldehydes And
Oxidation Of Allylic And Benzylic Alcohols To Aldehydes And
 Lialh4 And Nabh4 Carbonyl Reduction Mechanism In 2020 Chemistry
Lialh4 And Nabh4 Carbonyl Reduction Mechanism In 2020 Chemistry
 Oxidation Of Primary Alcohol To Yield Carboxylic Acid Youtube
Oxidation Of Primary Alcohol To Yield Carboxylic Acid Youtube
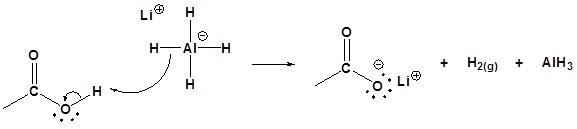 20 7 Reduction Of Carboxylic Acids And Their Derivatives
20 7 Reduction Of Carboxylic Acids And Their Derivatives
 Figure 1 From Biocatalytic Reduction Of Carboxylic Acids
Figure 1 From Biocatalytic Reduction Of Carboxylic Acids
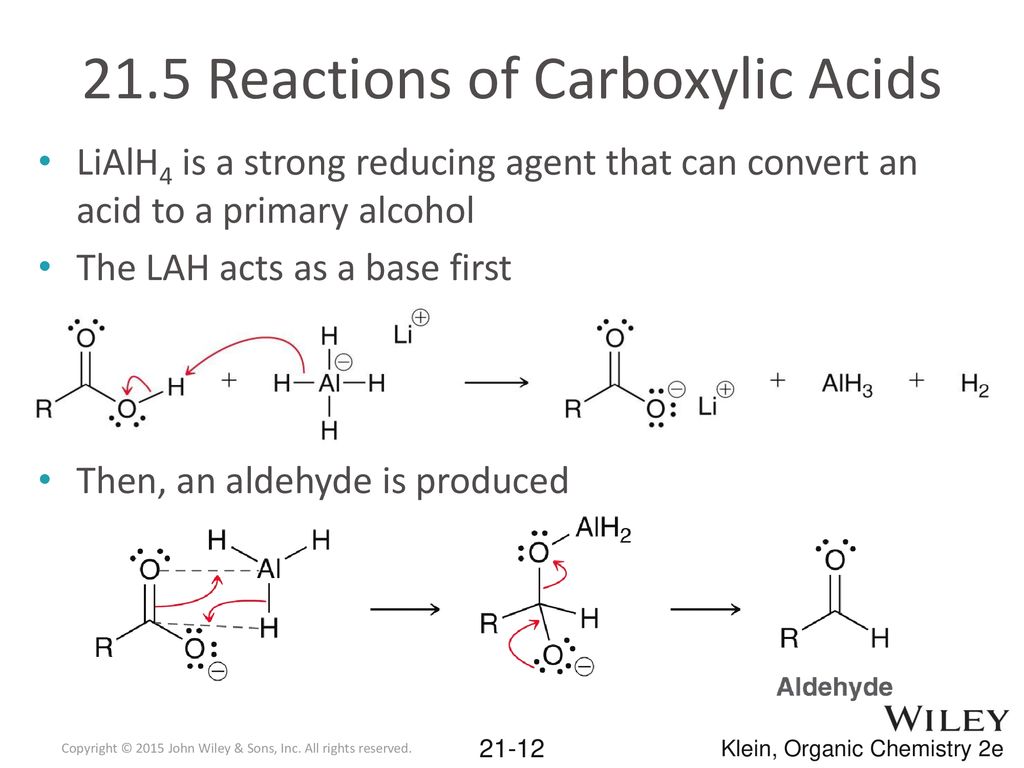 Carboxylic Acids And Their Derivatives Ppt Download
Carboxylic Acids And Their Derivatives Ppt Download
 Mechanism For Oxidation Of Primary Alcohols To Carboxylic Acids
Mechanism For Oxidation Of Primary Alcohols To Carboxylic Acids
 Nitrile Reduction Mechanism With Lialh4 And Dibal To Amine Or
Nitrile Reduction Mechanism With Lialh4 And Dibal To Amine Or
Oxidation Of Aldehydes To Carboxylic Acids Chemgapedia






Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar