Dna Polymerase 3 Functions
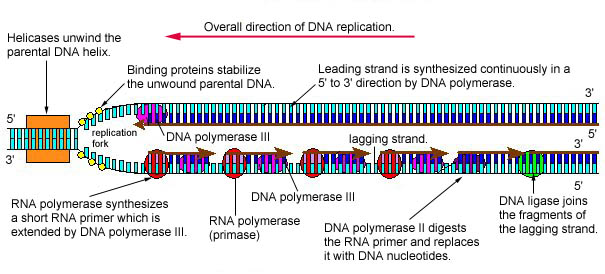
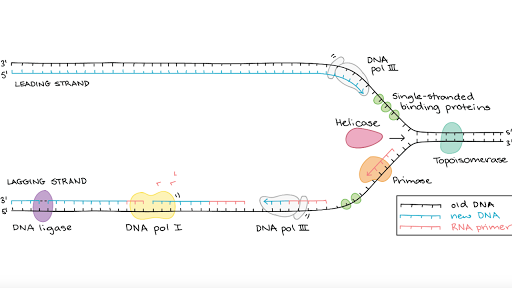
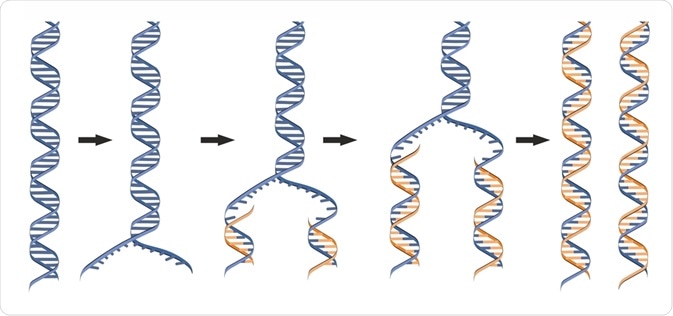
Before replication can take place an enzyme called helicase unwinds the dna molecule from its tightly woven form in the process breaking the hydrogen bond. Each enzyme replicates one of the two strands that comprise the dna double helix.
 Dna Replication And Types Of Dna
Dna Replication And Types Of Dna
Polymerase function during dna replication dna polymerase enzymes typically work in a pairwise fashion.
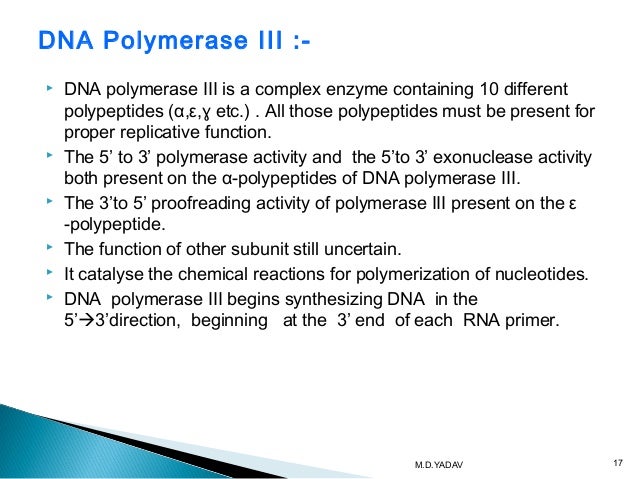
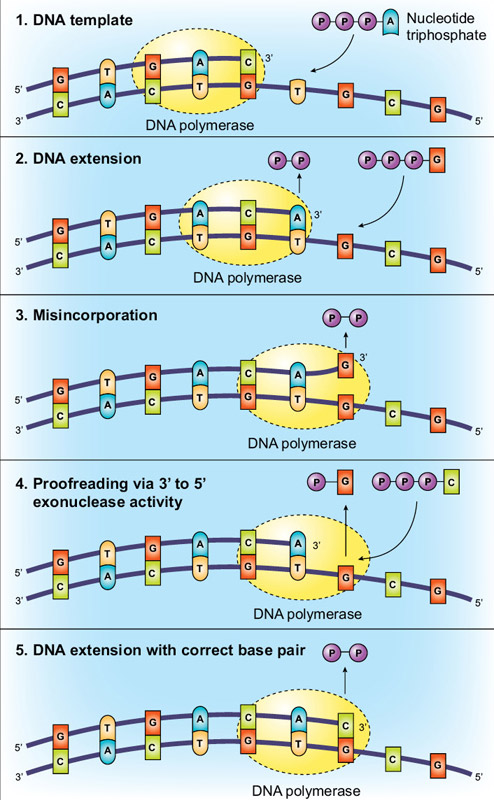
Dna polymerase 3 functions. The holoenzyme apoenzyme protein part coenzyme holoenzyme functions as a heterodimer of complexes at the replication fork with each monomer seeing to the synthesis of one daughter strand. Dna polymerase iii will then synthesize a continuous or discontinuous strand of dna depending if this is occurring on the leading or lagging strand okazaki fragment of the dna. Dna polymerase 3 possesses 5 to 3 polymerization activity where new nucleotides are added to the growing chain at its 3 end.
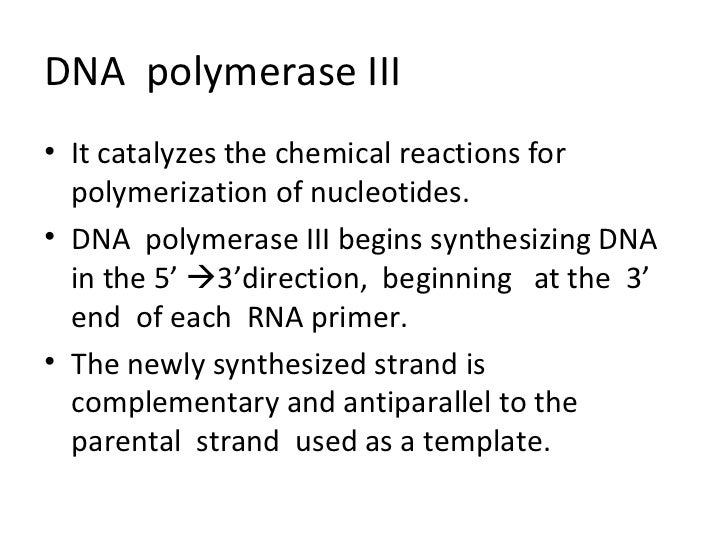
The main function of the third polymerase pol iii is duplication of the chromosomal dna while other dna polymerases are involved mostly in dna repair and translesion dna synthesis. The primary role of dna polymerases is to accurately and efficiently replicate the genome in order to ensure the maintenance of the genetic information and its faithful transmission through generations. The enzyme dna polymerase iii is the primary enzyme involved with bacterial dna replication.
Dna polymerase 3 is the main enzyme involved in prokaryotic dna replication. Every time a cell divides dna polymerases are required to duplicate the cell s dna so that a copy of the original dna molecule can be passed to each daughter cell. Dna polymerase iii is the principle replicative dna polymerase of e coli.
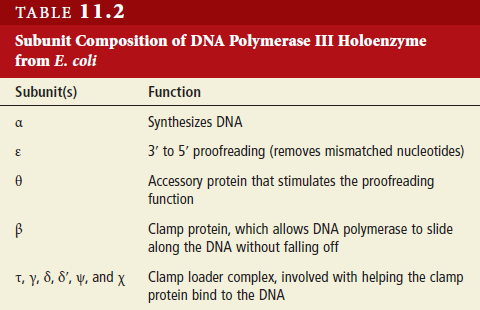
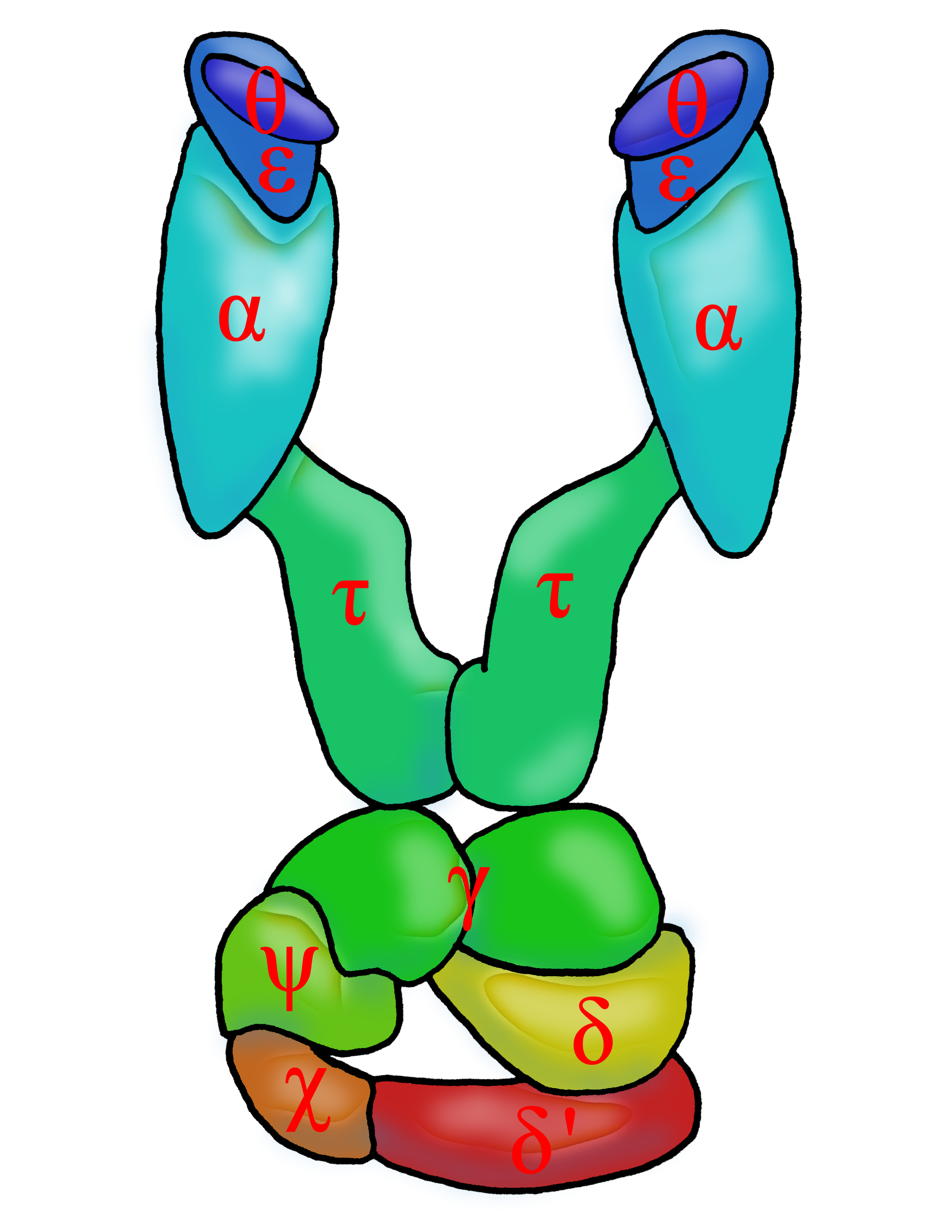
The dna polymerase iii holoenzyme is composed of 10 subunits. In this way genetic information is passed down from generation to generation. The enzyme aids the base pairing of incoming nucleotides with the template strand.
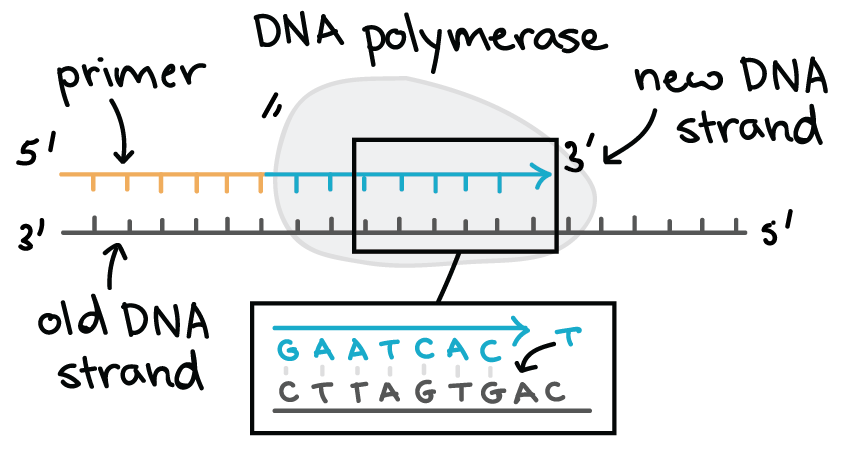
It performs the 5 3 polymerase function which means that it adds nucleotides to the 3 end of the forming dna strand during replication. Dna polymerase iii has a high processivity and therefore synthesizes dna very quickly. It is a multisubunit complex.
Together with a dna helicase and a primase pol iii he participates in the replicative apparatus that acts at the replication fork. Before replication can start the enzyme helicase unwinds the two dna strands. These enzymes cannot replace each other as both have different functions to be performed.
Dna polymerase adds nucleotides to the three prime end of a dna strand one nucleotide at a time. Both strands become templates for replication. α ε φ subunits core enzyme.
This is not a simple task considering the size of the genome and its constant exposure to endogenous and environmental dna damaging agents. Dna polymerase 3 is essential for the replication of the leading and the lagging strands whereas dna polymerase 1 is essential for removing of the rna primers from the fragments and replacing it with the required nucleotides. The core of the polymerase contains the catalytic polymerase subunit α the proofreading 3 5 exonuclease ε and a subunit of unknown function θ.
 Pdf Dna Polymerase Iii Holoenzyme Structure And Function Of A
Pdf Dna Polymerase Iii Holoenzyme Structure And Function Of A
 Anatomy Of A Polymerase How Function And Structure Are Related Neb
Anatomy Of A Polymerase How Function And Structure Are Related Neb
Dna Polymerase Iii Holoenzyme Html 11 T03 Dna Polymerase Iii
 Dna Replication Part 2 Enzymology Figure The Polymerization
Dna Replication Part 2 Enzymology Figure The Polymerization
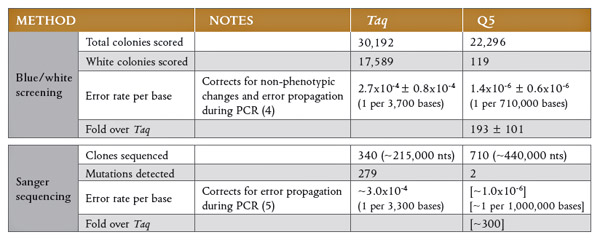 Polymerase Fidelity What Is It And What Does It Mean For Your
Polymerase Fidelity What Is It And What Does It Mean For Your
 Why Can T Dna Polymerase Initiate The Synthesis Of A New Dna
Why Can T Dna Polymerase Initiate The Synthesis Of A New Dna
 Dna Polymerase Definition Function Video Lesson Transcript
Dna Polymerase Definition Function Video Lesson Transcript
 Review Proteins And Their Function In The Early Stages Of
Review Proteins And Their Function In The Early Stages Of
 Dna Replication Of Prokaryotes Page 2
Dna Replication Of Prokaryotes Page 2
 So Many Dna Polymerases So Little Time Goldbio
So Many Dna Polymerases So Little Time Goldbio
 How Dna Polymerase Works Youtube
How Dna Polymerase Works Youtube
 Dna Polymerase Iii Holoenzyme Wikipedia
Dna Polymerase Iii Holoenzyme Wikipedia
 Dna Polymerase Structure Functions In Pro And Eukaryotes
Dna Polymerase Structure Functions In Pro And Eukaryotes
Difference Between Dna Polymerase 1 And 3 Difference Between
 Dna Polymerase Iii Enzyme Used During Replication Multisubunit
Dna Polymerase Iii Enzyme Used During Replication Multisubunit
 19 4 Dna Replication In Prokaryotic Cells Biology Libretexts
19 4 Dna Replication In Prokaryotic Cells Biology Libretexts
Difference Between Dna Polymerase 1 And 3 Definition Structure
Difference Between Rna Polymerase 1 2 And 3 Pediaa Com
Kevin Ahern S Biochemistry Course Bb 350 At Oregon State University
Http Mcb Berkeley Edu Courses Mcb110 Zhou Lec 5 7 Euk Trxn Apparatus Pdf
 Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy
 Enzymes And Proteins In Dna Replication
Enzymes And Proteins In Dna Replication
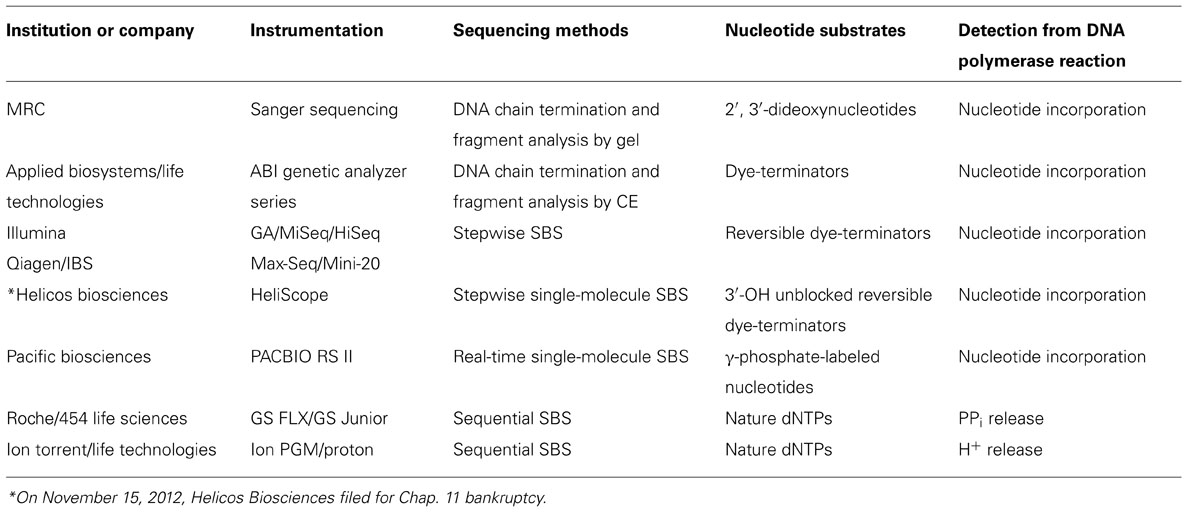 Frontiers Dna Polymerases Drive Dna Sequencing By Synthesis
Frontiers Dna Polymerases Drive Dna Sequencing By Synthesis
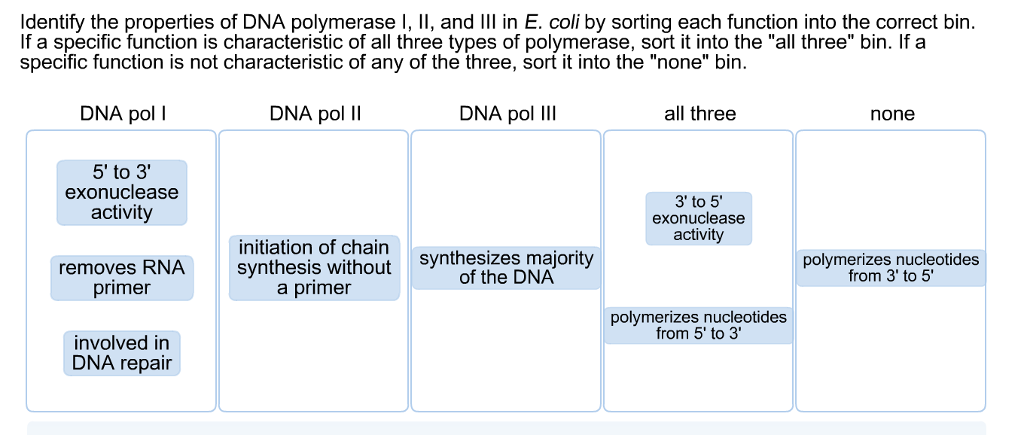 Solved Identify The Properties Of Dna Polymerase I Ii A
Solved Identify The Properties Of Dna Polymerase I Ii A
 Why Can T Dna Polymerase Initiate The Synthesis Of A New Dna
Why Can T Dna Polymerase Initiate The Synthesis Of A New Dna
Dna Polymerase I Worthington Enzyme Manual
 Dna Polymerase Enzymes A Close Look
Dna Polymerase Enzymes A Close Look
Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gcrahmkzwjx8h1jzlitowi Mo7y 2mlwssvzbcr9dcudocihyqod Usqp Cau
 Dna Polymerase Summary 1 Dna Replication Is Semi Conservative 2
Dna Polymerase Summary 1 Dna Replication Is Semi Conservative 2
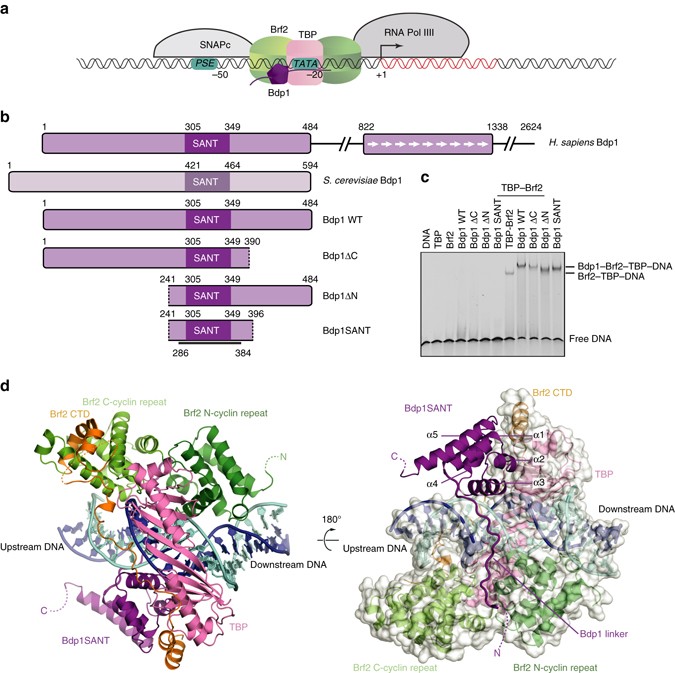 Molecular Mechanisms Of Bdp1 In Tfiiib Assembly And Rna Polymerase
Molecular Mechanisms Of Bdp1 In Tfiiib Assembly And Rna Polymerase





Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar