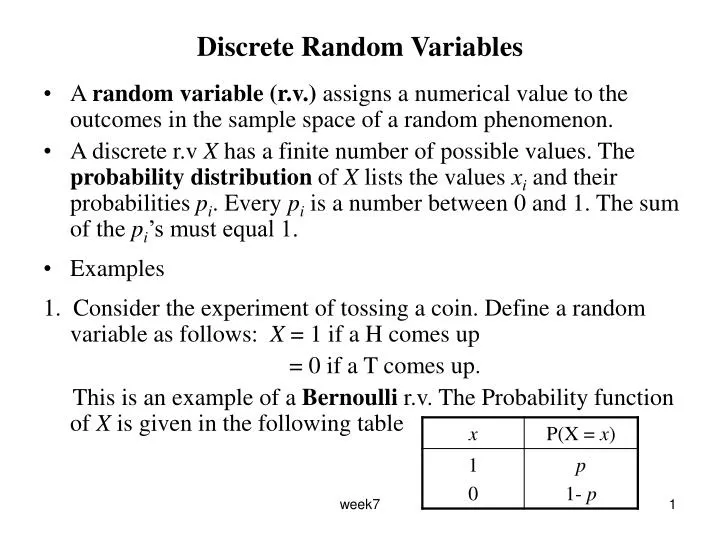
Discrete Random Variable Definition
A discrete variable is one that can take on finitely many or countably infinitely many values whereas a continuous random variable is one that is not discrete i e. Can take on uncountably infinitely many values such as a spectrum of real numbers.
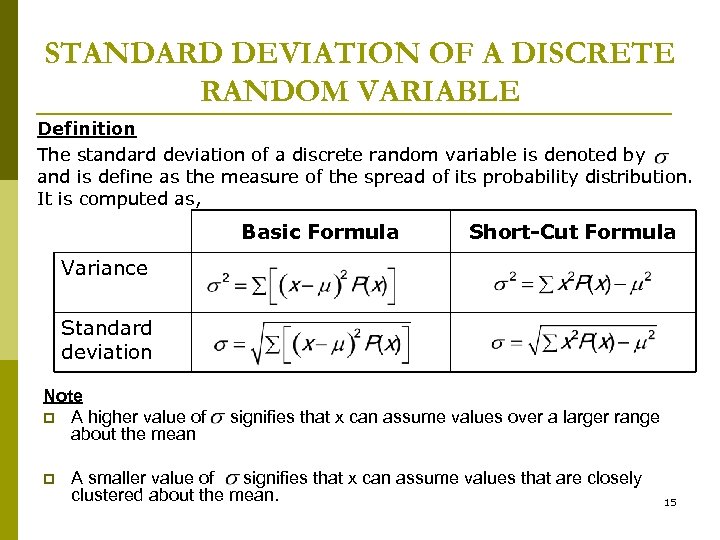 Chapter 5 Discrete Probability Distributions 1 2
Chapter 5 Discrete Probability Distributions 1 2
A random variable is a variable taking on numerical values determined by the outcome of a random phenomenon.

Discrete random variable definition. Definition a random variable is discrete if its support is countable and there exist a function called probability mass function of such that where is the probability that will take the value. Or continuous taking any numerical value in an interval or collection of intervals having an uncountable range via a probability density function that is characteristic of the random variable s probability distribution. A random variable is called continuous if its possible values contain a whole interval of numbers.
For example if a point a a is chosen uniformly at random in the interval. Discrete variables are the variables wherein the values can be obtained by counting. Number of students present.
Number of heads when flipping three coins. Or a mixture of both types. A random variable is a number generated by a random experiment.
A discrete variableis a variable whose value is obtained by counting. A discrete random variable is often said to have a discrete probability distribution. A random variable is called discrete if its possible values form a finite or countable set.
Random variables can be discrete that is taking any of a specified finite or countable list of values having a countable range endowed with a probability mass function characteristic of the random variable s probability distribution. Your pythagorean x is a good example. A discrete random variable is finite if its list of possible values has a fixed finite number of elements in it for example the number of smoking ban supporters in a random sample of 100 voters has to be between 0 and 100.
Number of red marbles in a jar. A random variable is a variable whose value is unknown or a function that assigns values to each of an experiment s outcomes. On the other hand continuous variables are the random variables that measure something.
Discrete variable assumes independent values whereas continuous variable assumes any value in a given range or continuum. The probability distribution of a random variable x x tells us what the possible values of x x are and what probabilities are assigned to those values. However this does not imply that the sample space must have at most countably infinitely many outcomes.
A discrete random variable is a random variable which takes only finitely many or countably infinitely many different values. Random variables are often designated by letters and can be classified. One very common finite random variable is obtained from the binomial distribution.
A discrete random variable has a countable number of possible values.
 Solved 5 The Discrete Random Variable X Has Probability
Solved 5 The Discrete Random Variable X Has Probability
 Cumulative Distribution Function Of A Discrete Random Variable
Cumulative Distribution Function Of A Discrete Random Variable
 Independent Discrete Random Variables Mathematics Stack Exchange
Independent Discrete Random Variables Mathematics Stack Exchange
 Discrete Random Variables And Probability Distributions
Discrete Random Variables And Probability Distributions
 Solved Problem 4 40 Points For A Discrete Random Varia
Solved Problem 4 40 Points For A Discrete Random Varia
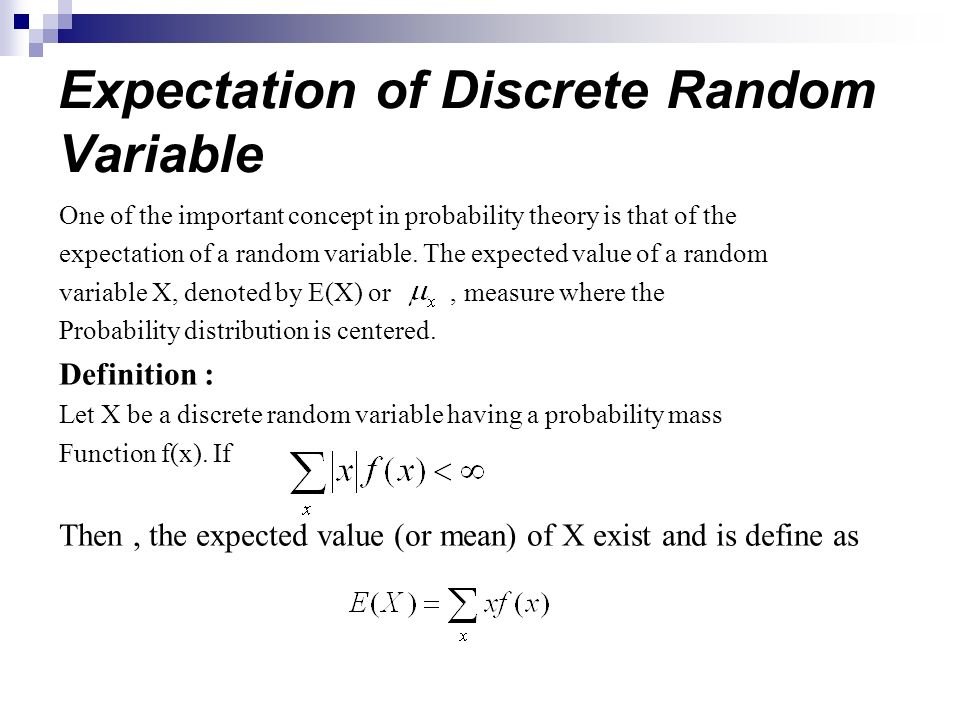 Chapter Eight Expectation Of Discrete Random Variable Ppt Video
Chapter Eight Expectation Of Discrete Random Variable Ppt Video
 Discrete Random Variables By محمد حسب الله رزالي Issuu
Discrete Random Variables By محمد حسب الله رزالي Issuu
 Discrete And Continuous Random Variables Download Scientific Diagram
Discrete And Continuous Random Variables Download Scientific Diagram
 Problem 1 Let X Be A Discrete Random Variable With Values 2 0 1
Problem 1 Let X Be A Discrete Random Variable With Values 2 0 1
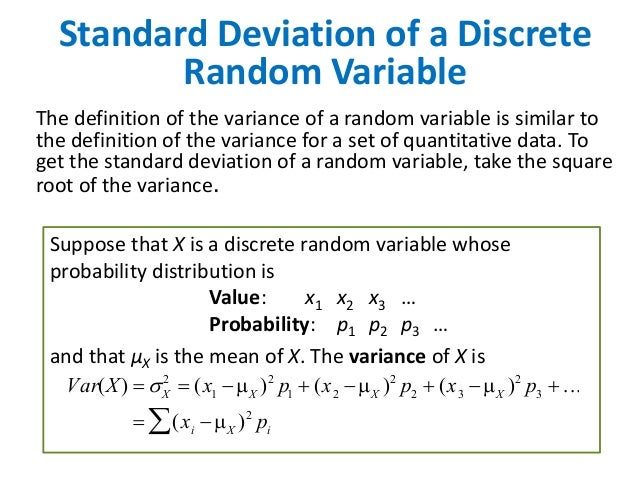 Discrete And Continuous Random Variables
Discrete And Continuous Random Variables
 Maths For Ml Probability Distributions By Raghunath D Medium
Maths For Ml Probability Distributions By Raghunath D Medium
 Exam Questions Discrete Random Variables Examsolutions
Exam Questions Discrete Random Variables Examsolutions
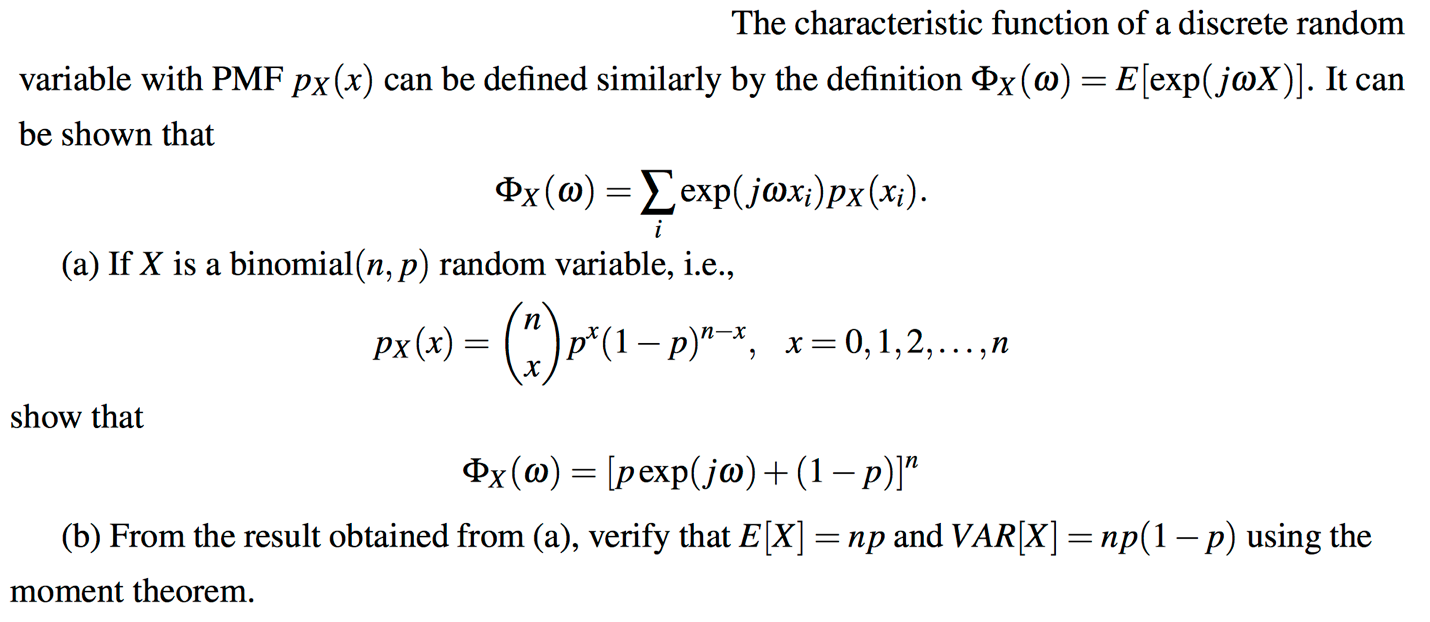 Solved The Characteristic Function Of A Discrete Random V
Solved The Characteristic Function Of A Discrete Random V

 Chapter 2 Discrete Random Variables Ppt Video Online Download
Chapter 2 Discrete Random Variables Ppt Video Online Download
Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gctir6yupmf6ukjnktbh9s3xpcwo 7z9cohhs861 Xwp0dgznnj0 Usqp Cau
 Discrete And Continuous Random Variables
Discrete And Continuous Random Variables
 Maths M1 Chp11 Discrete Random Variables Ans By Patrick Ho Issuu
Maths M1 Chp11 Discrete Random Variables Ans By Patrick Ho Issuu
 Ppt Discrete Random Variables Powerpoint Presentation Free
Ppt Discrete Random Variables Powerpoint Presentation Free
 Chapter 4 Discrete Random Variables
Chapter 4 Discrete Random Variables
 5 1 Two Discrete Random Variables Example Two Discrete Random
5 1 Two Discrete Random Variables Example Two Discrete Random
 Probability Random Variables Preparatory Notes Prezentaciya Onlajn
Probability Random Variables Preparatory Notes Prezentaciya Onlajn
 Discrete Random Variables Boundless Statistics
Discrete Random Variables Boundless Statistics
 Discrete And Continuous Random Variables Video Khan Academy
Discrete And Continuous Random Variables Video Khan Academy
 1 Engineering Statistics Ie 261 Chapter 3 Discrete Random
1 Engineering Statistics Ie 261 Chapter 3 Discrete Random
 Chapter 4 Part2 Random Variables
Chapter 4 Part2 Random Variables
 Prove Variance Shortcut Method For Discrete Random Variable Youtube
Prove Variance Shortcut Method For Discrete Random Variable Youtube
 Chapter 2 Chapter 2 Discrete Random Variables Discrete Random
Chapter 2 Chapter 2 Discrete Random Variables Discrete Random
Https Ocw Mit Edu Resources Res 6 012 Introduction To Probability Spring 2018 Part I The Fundamentals Mitres 6 012s18 L05 Pdf
Discrete And Continuous Random Variables
 Solved 4 Suppose That X And Y Are Independent Discrete R
Solved 4 Suppose That X And Y Are Independent Discrete R
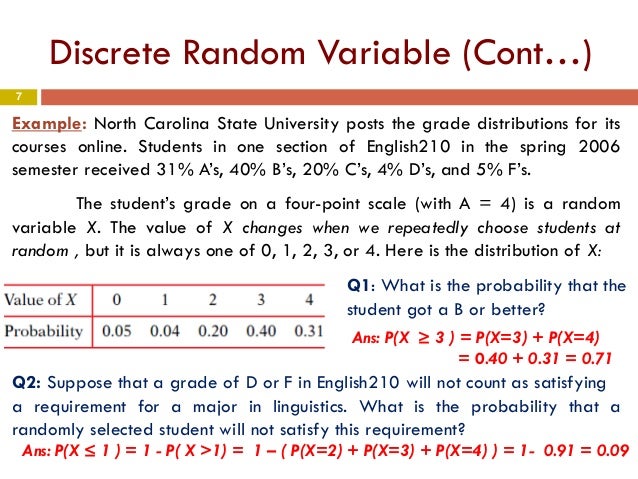
 Probability Distributions For Discrete Random Variables Example
Probability Distributions For Discrete Random Variables Example
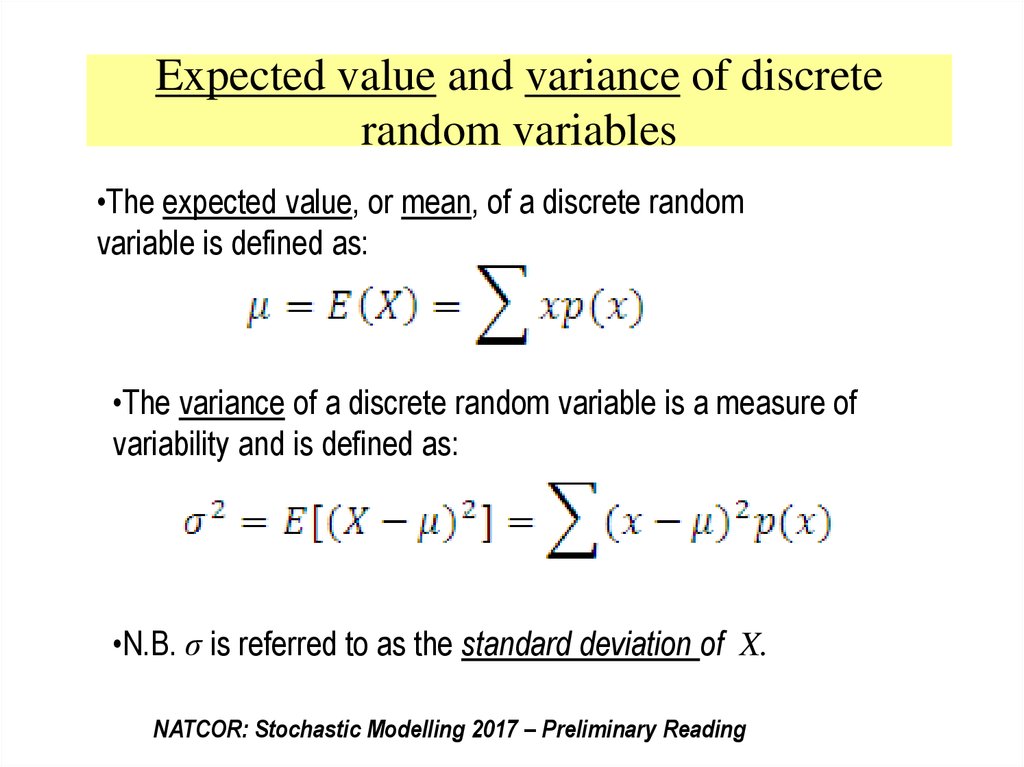
Variance And Standard Deviation Of Discrete Random Variables




Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar