Dna Polymerase 3 Function In Dna Replication
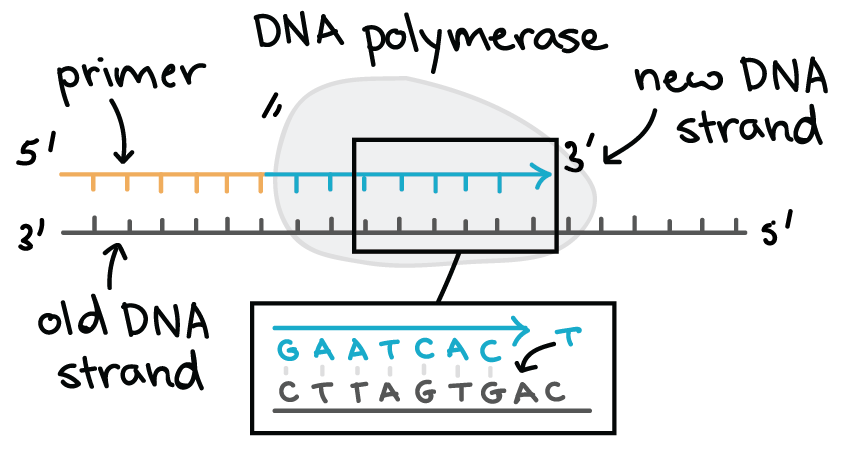
Definition of dna polymerase dna polymerase also refers as dna replicase which forms dna by adding nucleotides in the replication process. Dna polymerase adds nucleotides to the three prime end of a dna strand one nucleotide at a time.
Dna polymerases are specially designed enzymes which help in formation of dna molecules by assembling tiny building blocks of dna called as nucleotides.

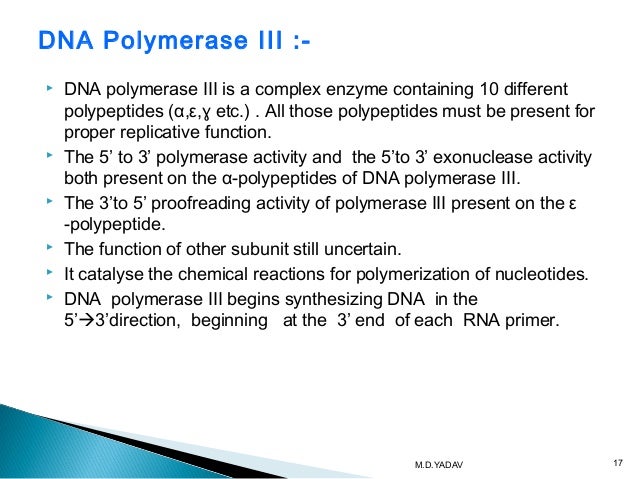
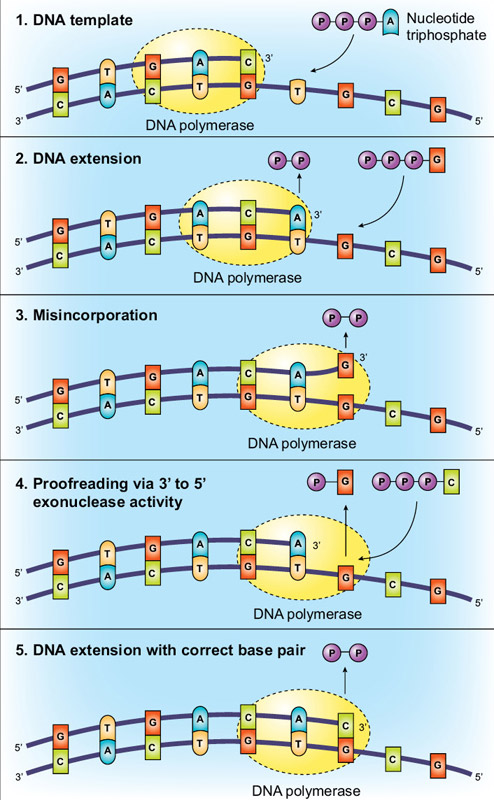
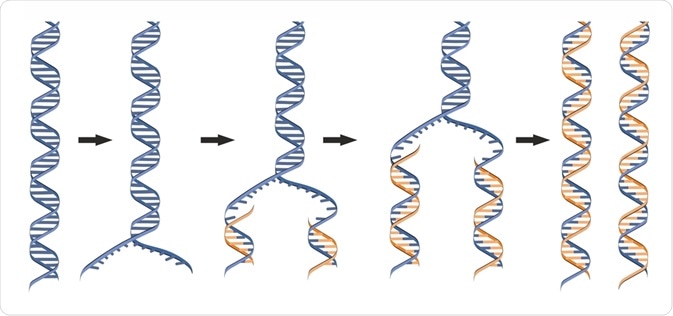
Dna polymerase 3 function in dna replication. Dna polymerases in prokaryotes. Proofreading helps to maintain the integrity of the double stranded dna. Both strands become templates for replication.
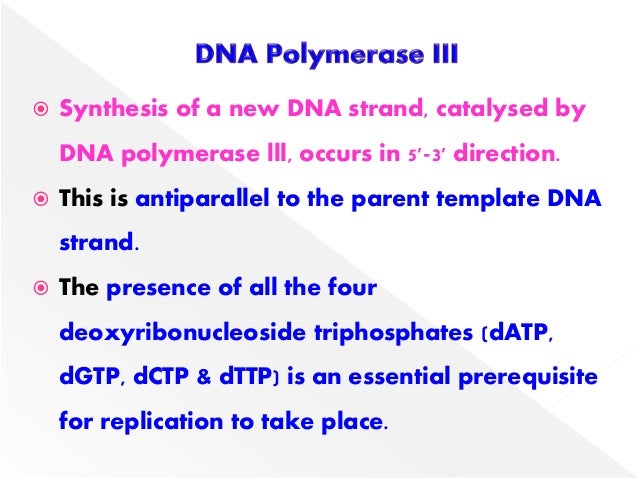
The holoenzyme apoenzyme protein part coenzyme holoenzyme functions as a heterodimer of complexes at the replication fork with each monomer seeing to the synthesis of one daughter strand. Dna polymerase performs several functions during replication. Polymerase enzyme always moves along with the parental strand template strand in 3 5 direction but forms daughter strand complementary strand in 5 3 direction.
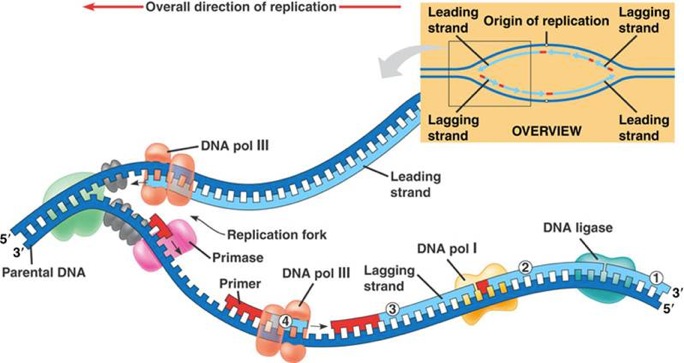
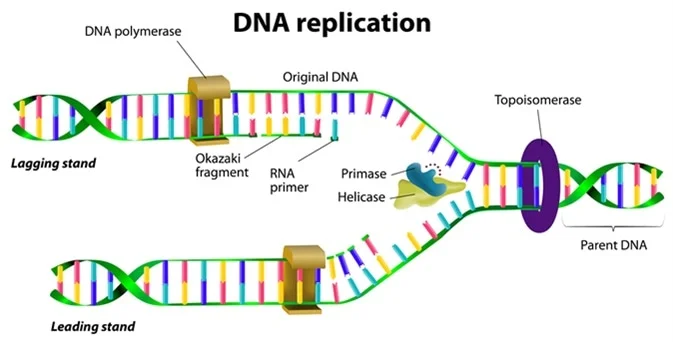
Before replication can start the enzyme helicase unwinds the two dna strands. It is a multisubunit complex. The enzyme dna polymerase iii is the primary enzyme involved with bacterial dna replication.
α ε φ subunits core enzyme. The main function of dna polymerase is to synthesize a new dna strand. Before replication can take place an enzyme called helicase unwinds the dna molecule from its tightly woven form in the process breaking the hydrogen bond.
Dna polymerase iii is the principle replicative dna polymerase of e coli. Apart from this dna polymerase is also involved in correcting the errors of added nucleotides in a process known as proofreading. Dna polymerase helps in splitting of the dna molecule into two identical dnas.
This process of dna splitting is called as dna replication. It performs the 5 3 polymerase function which means that it adds nucleotides to the 3 end of the forming dna strand during replication. In this way genetic information is passed down from generation to generation.
Every time a cell divides dna polymerases are required to duplicate the cell s dna so that a copy of the original dna molecule can be passed to each daughter cell.
 Why Can T Dna Polymerase Initiate The Synthesis Of A New Dna
Why Can T Dna Polymerase Initiate The Synthesis Of A New Dna
 Dna Polymerase I An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Dna Polymerase I An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
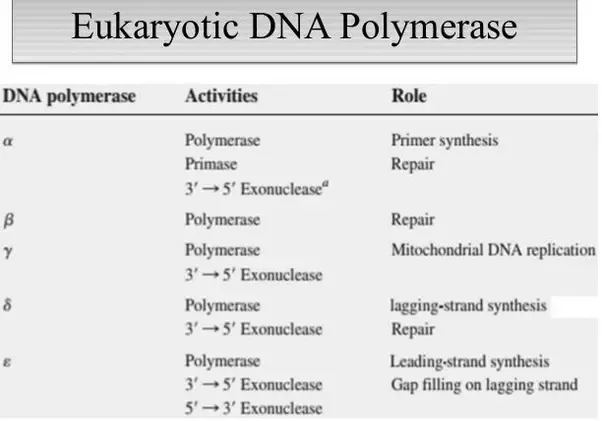
 Dna Polymerase Structure Functions In Pro And Eukaryotes
Dna Polymerase Structure Functions In Pro And Eukaryotes
 Review Proteins And Their Function In The Early Stages Of
Review Proteins And Their Function In The Early Stages Of
Difference Between Dna Polymerase 1 And 3 Definition Structure
 Dna Polymerase Iii Enzyme Used During Replication Multisubunit
Dna Polymerase Iii Enzyme Used During Replication Multisubunit
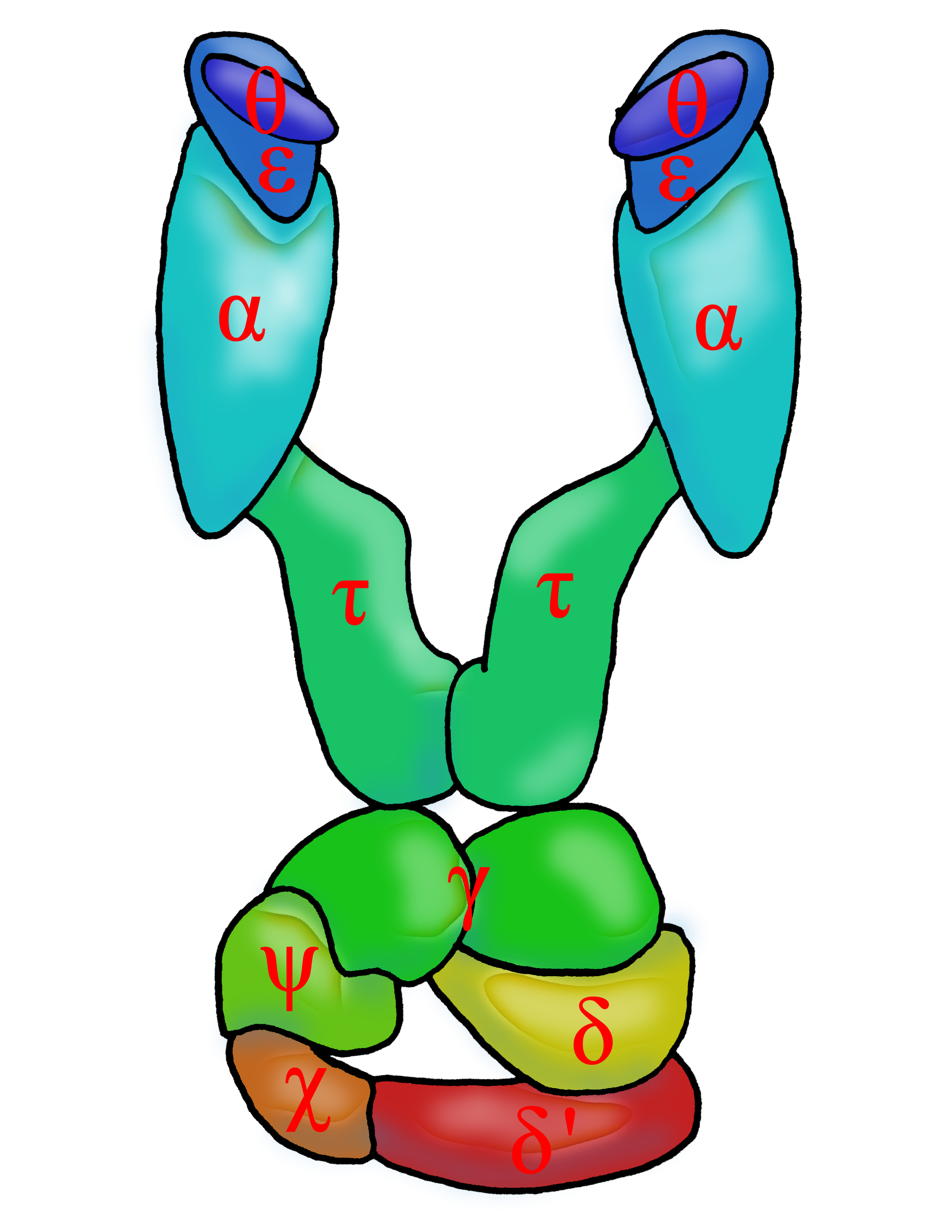 Dna Polymerase Iii Holoenzyme Wikipedia
Dna Polymerase Iii Holoenzyme Wikipedia
 Dna Polymerase 1 2 And 3 Youtube
Dna Polymerase 1 2 And 3 Youtube
Polymerases Biology Libretexts
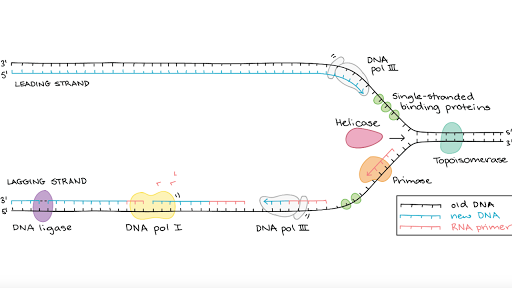
 Dna Replication Part 2 Of 3 Dna Polymerases Prokaryotes And
Dna Replication Part 2 Of 3 Dna Polymerases Prokaryotes And
Kevin Ahern S Biochemistry Bb 451 551 At Oregon State University
Difference Between Dna Polymerase 1 And 3 Difference Between
 Enzymes And Proteins In Dna Replication
Enzymes And Proteins In Dna Replication
 Enzymes Involved In Replication Some Enzymes Involved In Dna
Enzymes Involved In Replication Some Enzymes Involved In Dna
 1 Dna Replication Is Semi Conservative 2 Dna Polymerase Enzymes
1 Dna Replication Is Semi Conservative 2 Dna Polymerase Enzymes
 Lecture 2 Chapter 11 Dna Replication Ppt Download
Lecture 2 Chapter 11 Dna Replication Ppt Download
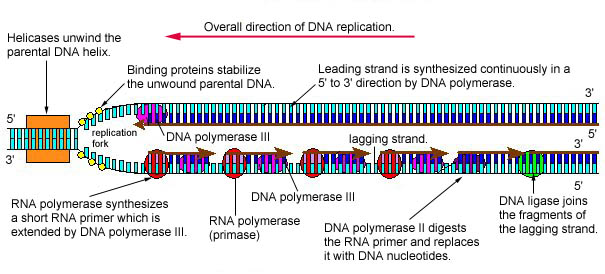 19 4 Dna Replication In Prokaryotic Cells Biology Libretexts
19 4 Dna Replication In Prokaryotic Cells Biology Libretexts
 Dna Replication Part 2 Enzymology Figure The Polymerization
Dna Replication Part 2 Enzymology Figure The Polymerization
 Dna Replication And Types Of Dna
Dna Replication And Types Of Dna
 Anatomy Of A Polymerase How Function And Structure Are Related Neb
Anatomy Of A Polymerase How Function And Structure Are Related Neb
 Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy
 Why Can T Dna Polymerase Initiate The Synthesis Of A New Dna
Why Can T Dna Polymerase Initiate The Synthesis Of A New Dna
 How Dna Polymerase Works Youtube
How Dna Polymerase Works Youtube
 Dna Polymerase Enzymes A Close Look
Dna Polymerase Enzymes A Close Look
 Polymerase Fidelity What Is It And What Does It Mean For Your
Polymerase Fidelity What Is It And What Does It Mean For Your
 Dna Polymerase Definition Function Video Lesson Transcript
Dna Polymerase Definition Function Video Lesson Transcript
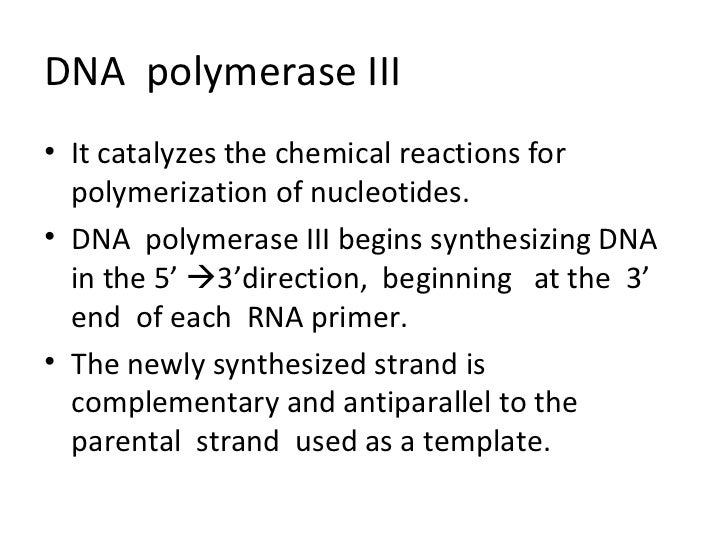 Enzymes And Proteins In Dna Replication
Enzymes And Proteins In Dna Replication
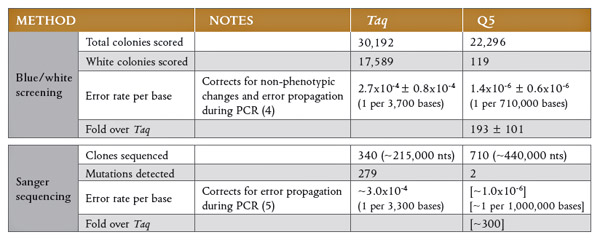
 So Many Dna Polymerases So Little Time Goldbio
So Many Dna Polymerases So Little Time Goldbio
Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gcrhitczqvraw5hnm9alxb5jsleok Ibljxuyz4lveou4rxzpsx Usqp Cau





Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar