Above The Critical Temperature A Substance
The pressure required to liquify a substance vapor at its critical temperature. A molten salt is a salt heated to its melting point giving a stable liquid that conducts electricity.
10 13 Critical Temperature And Pressure Chemistry Libretexts
Two types of liquid liquid critical points are the upper critical solution temperature ucst which is the hottest point at which cooling will induce phase separation and the lower critical solution temperature lcst which is the coldest point at which heating will induce phase separation.
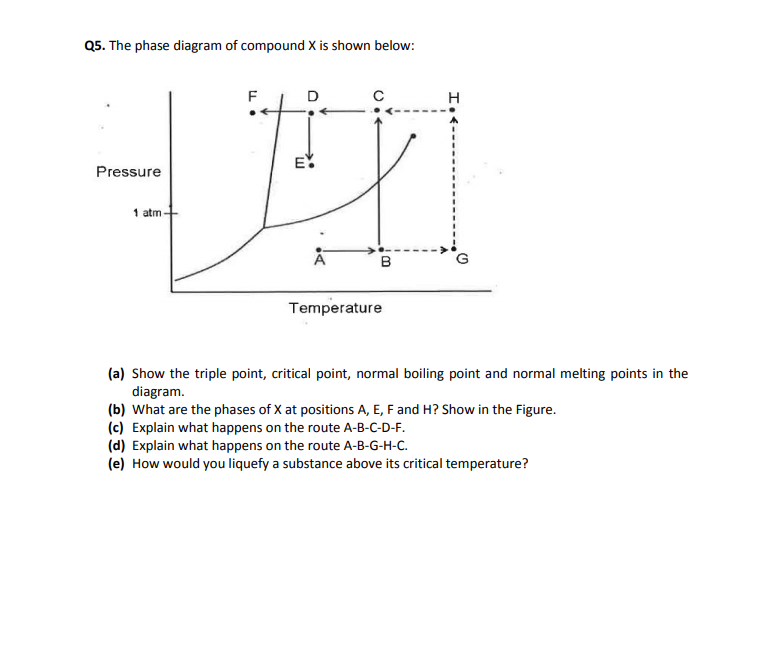
Above the critical temperature a substance. At the critical temperature they cannot longer be liquified. The critical temperature of a substance is the temperature at and above which vapor of the substance cannot be liquefied no matter how much pressure is applied. Above the critical temperature and pressure a substance exists as a dense fluid called a supercritical fluid which resembles a gas in that it completely fills its container but has a density comparable to that of a liquid.
Some examples are shown below. The temperature which above a substance can not exist as a liquid no matter how much pressure is applied. It can effuse through solids like a gas and dissolve materials like a liquid.
Every substance has a critical temperature. If the temperature is below critical temp and the pressure is also below its critical value then there is a possibility that we see an equilibrium between the liquid and gaseous states. A supercritical fluid scf is any substance at a temperature and pressure above its critical point where distinct liquid and gas phases do not exist.
When one of them is above their critical value it is impossible to change the state of the substance from gas to liquid by merely changing the other parameter. Every substance has a critical temperature. For instance if t t c then no matter how much you try to increase the pressure the gas will not liquefy.
 Critical Point Chemistry Dictionary Glossary
Critical Point Chemistry Dictionary Glossary
 What Is Critical Temperature Short Definition Plz Tell Brainly In
What Is Critical Temperature Short Definition Plz Tell Brainly In
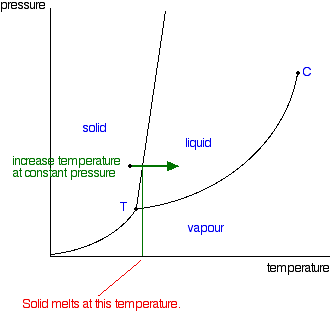 Phase Diagrams Of Pure Substances
Phase Diagrams Of Pure Substances
1 5 Phase Changes University Physics Volume 2 Openstax
Https Www Lamar Edu Arts Sciences Files Documents Chemistry Biochemistry Dorris 1412exam2 Pdf
 Critical Point Definition Chemistry
Critical Point Definition Chemistry
What Is Critical Temperature Pls Explain The Phenomenon Quora
 Supercritical Fluid Chromatography Quantitative Analysis
Supercritical Fluid Chromatography Quantitative Analysis
 Chapter 2b Pure Substances Ideal Gas Updated 1 17 11
Chapter 2b Pure Substances Ideal Gas Updated 1 17 11
 Liquid Behaviour Of Pure Liquids Britannica
Liquid Behaviour Of Pure Liquids Britannica
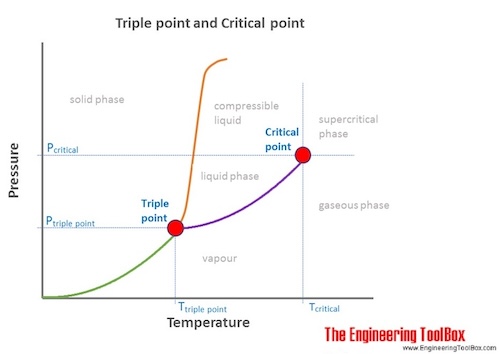
Difference Between Critical Point And Triple Point Definitions
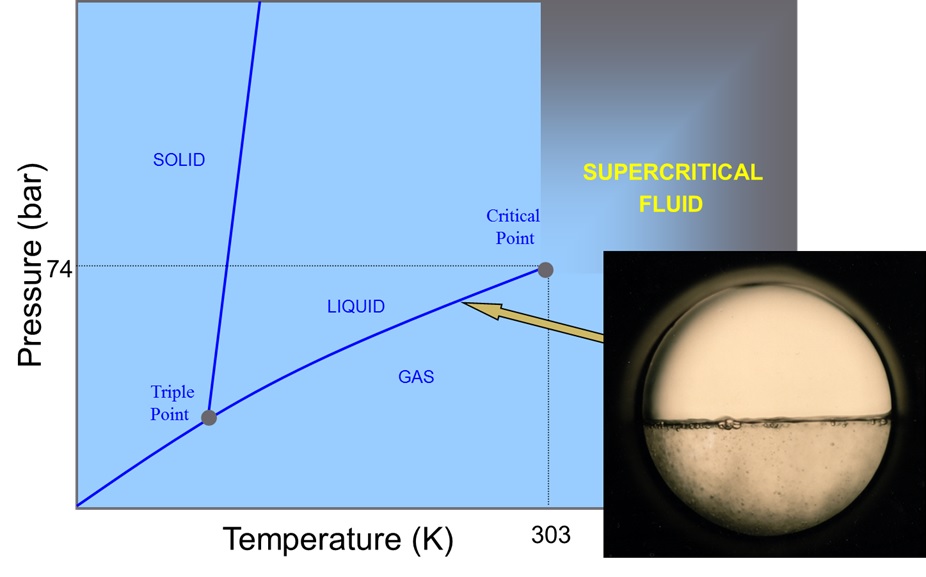 What Is A Supercritical Fluid Scimed
What Is A Supercritical Fluid Scimed
What Is The Definition Of Critical Pressure And Critical
Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gcte3bldophwpbuce8rpmfptirvoxaolgpevnlltf1onqgbod 70 Usqp Cau
 Critical Temperatures And Pressures For Some Common Substances
Critical Temperatures And Pressures For Some Common Substances
 Changes Of State Matter On Earth Can Exist In Any Of These States
Changes Of State Matter On Earth Can Exist In Any Of These States

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/phasediagram-56a129b35f9b58b7d0bca3ea.jpg) Critical Point Definition Chemistry
Critical Point Definition Chemistry
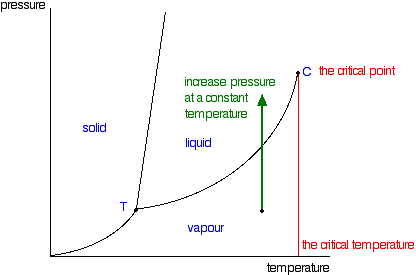 Phase Diagrams Of Pure Substances
Phase Diagrams Of Pure Substances
 Solved Q5 The Phase Diagram Of Compound X Is Shown Below
Solved Q5 The Phase Diagram Of Compound X Is Shown Below
 Phase Diagram For Water Chemistry For Non Majors
Phase Diagram For Water Chemistry For Non Majors
 Critical Temperature An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Critical Temperature An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Supercritical Fluids Introduction To Chemistry
Supercritical Fluids Introduction To Chemistry
 What Is The Difference Between Critical Temperature And Boiling
What Is The Difference Between Critical Temperature And Boiling
 Phase Diagrams Ap Chemistry Properties Of Liquids
Phase Diagrams Ap Chemistry Properties Of Liquids
/phasediagram-56a129b35f9b58b7d0bca3ea.jpg) Critical Point Definition Chemistry
Critical Point Definition Chemistry
 Reservior Fluids Hw 2 Reservoir Fluid Properties Lsu Studocu
Reservior Fluids Hw 2 Reservoir Fluid Properties Lsu Studocu
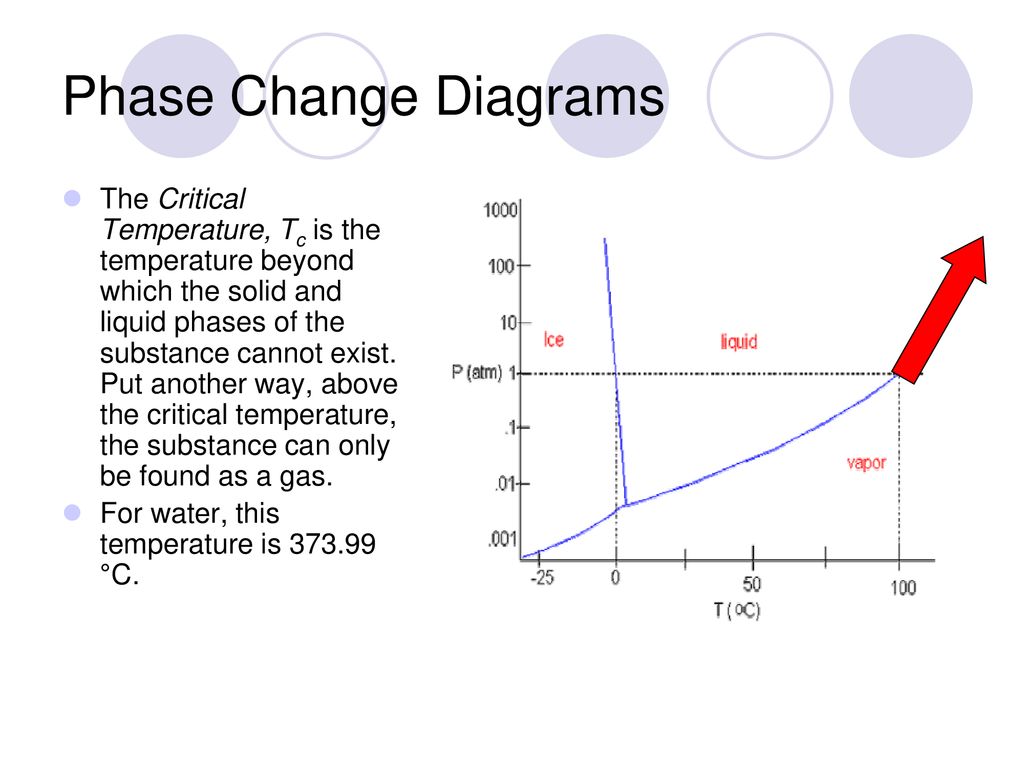 Matter In Motion Chapter 2 1 And Chapter Ppt Download
Matter In Motion Chapter 2 1 And Chapter Ppt Download
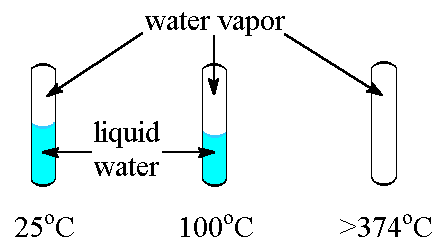 Critical Temperature And Pressure
Critical Temperature And Pressure
 Critical Point Thermodynamics Wikipedia
Critical Point Thermodynamics Wikipedia
 Chapter 10 States Of Matter Ppt Download
Chapter 10 States Of Matter Ppt Download




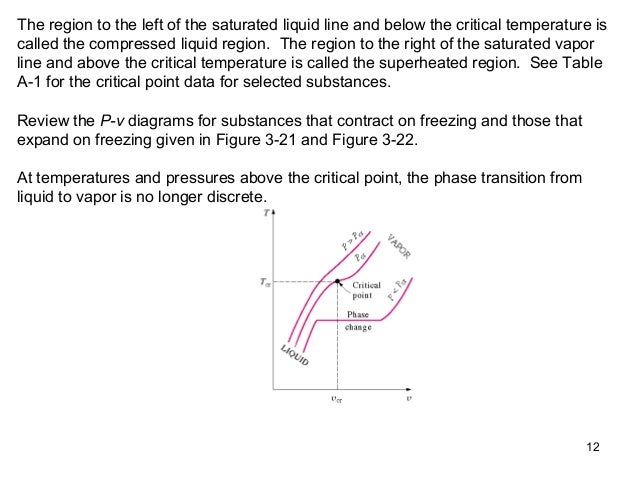
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar