How Does Glucose Enter The Cell
Active transport proteins use adenosine triphosphate atp the cell s energy storage molecule to pump glucose into the cell either with or against the concentration gradient. Could someone explain how does the nutrient molecule enter the extracellular space from the blood vessel.
 Why Can T Glucose Pass Directly Through The Plasma Membrane Quora
Why Can T Glucose Pass Directly Through The Plasma Membrane Quora
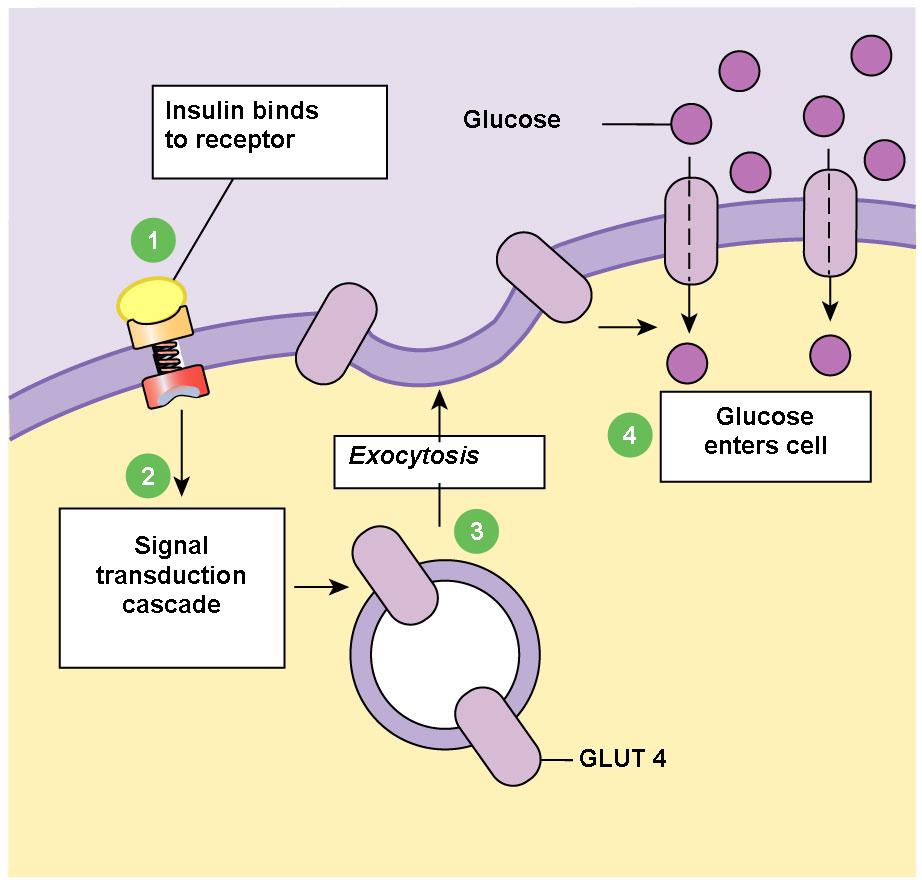
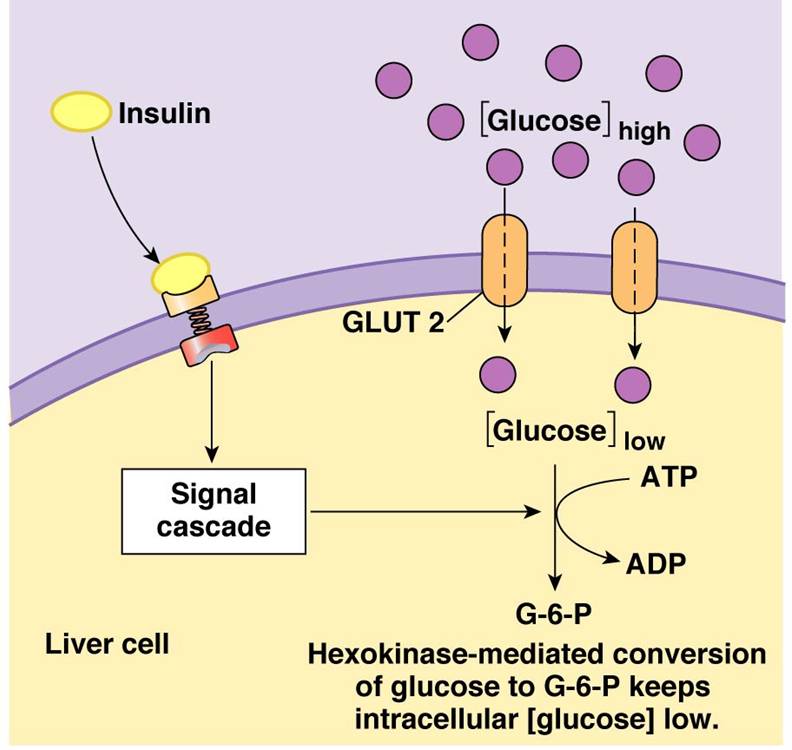
When insulin is released from the pancreas it travels through the bloodstream to the body s cells and tells the cell doors to open up to let the glucose in.
How does glucose enter the cell. After reaching the inside of the cell the cells machinery converts the sugar into energy. The first explains dr. Insulin is a hormone that moves glucose from your blood into the cells for energy and storage.
The cells along the small intestine use primary active transport to ensure that glucose only flows one way. Glucose enters the cell against the concentration gradient by active transport. The second is the hormone insulin which the pancreas releases into the bloodstream to help cells absorb glucose from the blood.
As glucose moves from the bloodstream into the cells blood sugar levels start to drop. In fact glucose takes part in a process of cotransport along with an ion such as na. Glucose is too large to dissolve through the membrane but there are integral proteins termed glut that utilize glucose concentrations to move glucose in passively.
The transporters in the plasma membrane of the cells promote the entry of glucose molecules from the extracellular matrix to the cytosol of the cell. For instance in the context of the pancreas the walls of the blood vessel is fenestrated. Glucose in the gi tract can also enter the cell through secondary active transport where sodium gradient inside the cell drives a trans membrane protein to import glucose with it.
When the sodium ion binds to the receptor the binding of glucose is also stimulated despite its concentration gradient. Once inside the cells convert glucose into energy to use right then or store it to use later. Oxygen enters the cells through simple diffusion while glucose amino acids and other large insoluble compounds enter through facilitated diffusion.
As it travels through your bloodstream to your cells it s called blood glucose or blood sugar. Sherwood is called a glucose transporter or glut protein. Glucose molecules enter a cell through its channel protein or gate.
Large molecules like glucose are too large to slide through pores in the membrane so it relies on the gates. Glucose from the bloodstream enters cells with the help of two proteins. Oxygen and glucose are carried in the bloodstream and enter individual cells by passing through the cell membrane via diffusion.
From digested food to the inside of cells. When cells require energy the glut molecule on the cell s surface will bind with blood glucose and usher it into the cell.
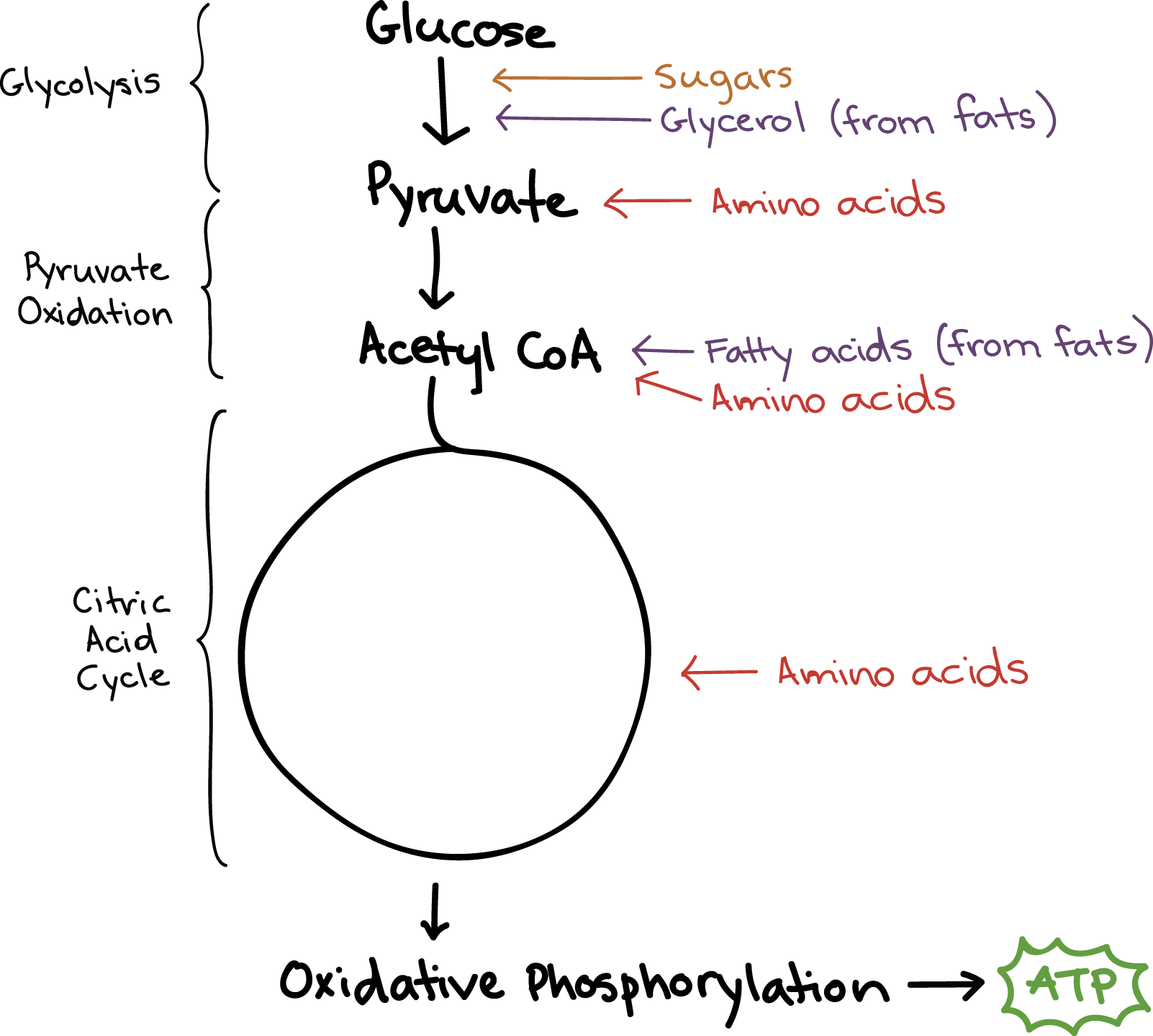 Connections Between Cellular Respiration And Other Pathways
Connections Between Cellular Respiration And Other Pathways
What Is Insulin Test Procedure And Results
 Glucose Transport From Liver To Blood Cell Youtube
Glucose Transport From Liver To Blood Cell Youtube
 Diabetes Type 1 In Depth Report Medtalk
Diabetes Type 1 In Depth Report Medtalk
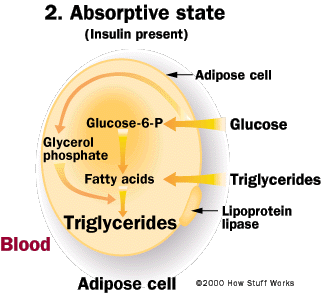 Fat Storage How Fat Cells Work Howstuffworks
Fat Storage How Fat Cells Work Howstuffworks
 Diabetes And Your Child Type 1 Understanding
Diabetes And Your Child Type 1 Understanding
Glucose Regulation And Utilization In The Body
 How Does Active Transport Allow Sugar Molecules To Enter Cells
How Does Active Transport Allow Sugar Molecules To Enter Cells
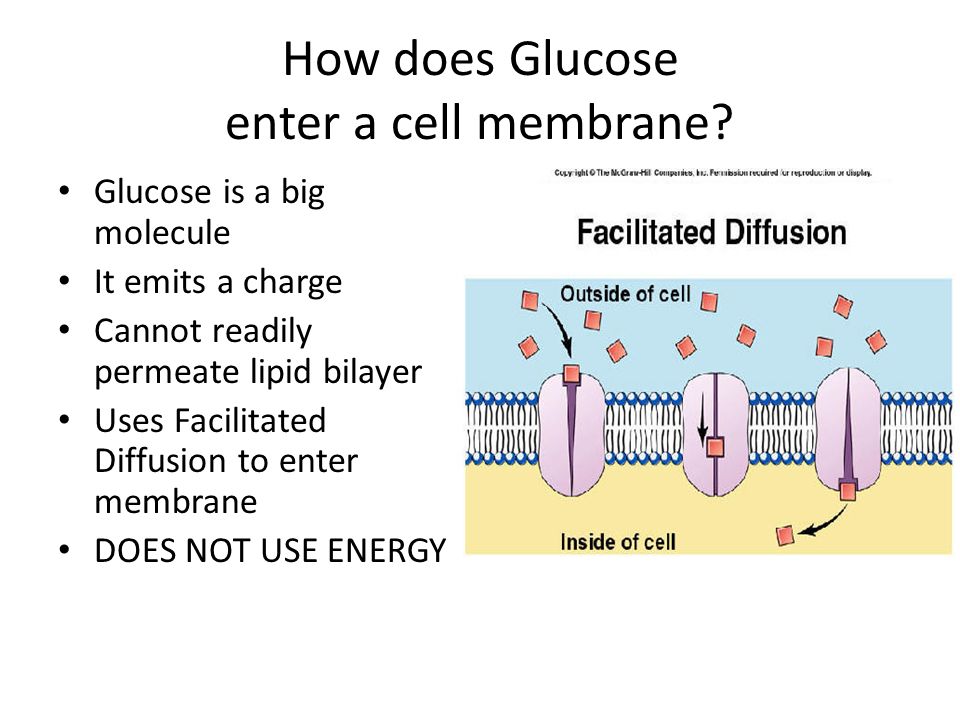 Aim What Is Diffusion Do Now Predict What Will Happen With The
Aim What Is Diffusion Do Now Predict What Will Happen With The
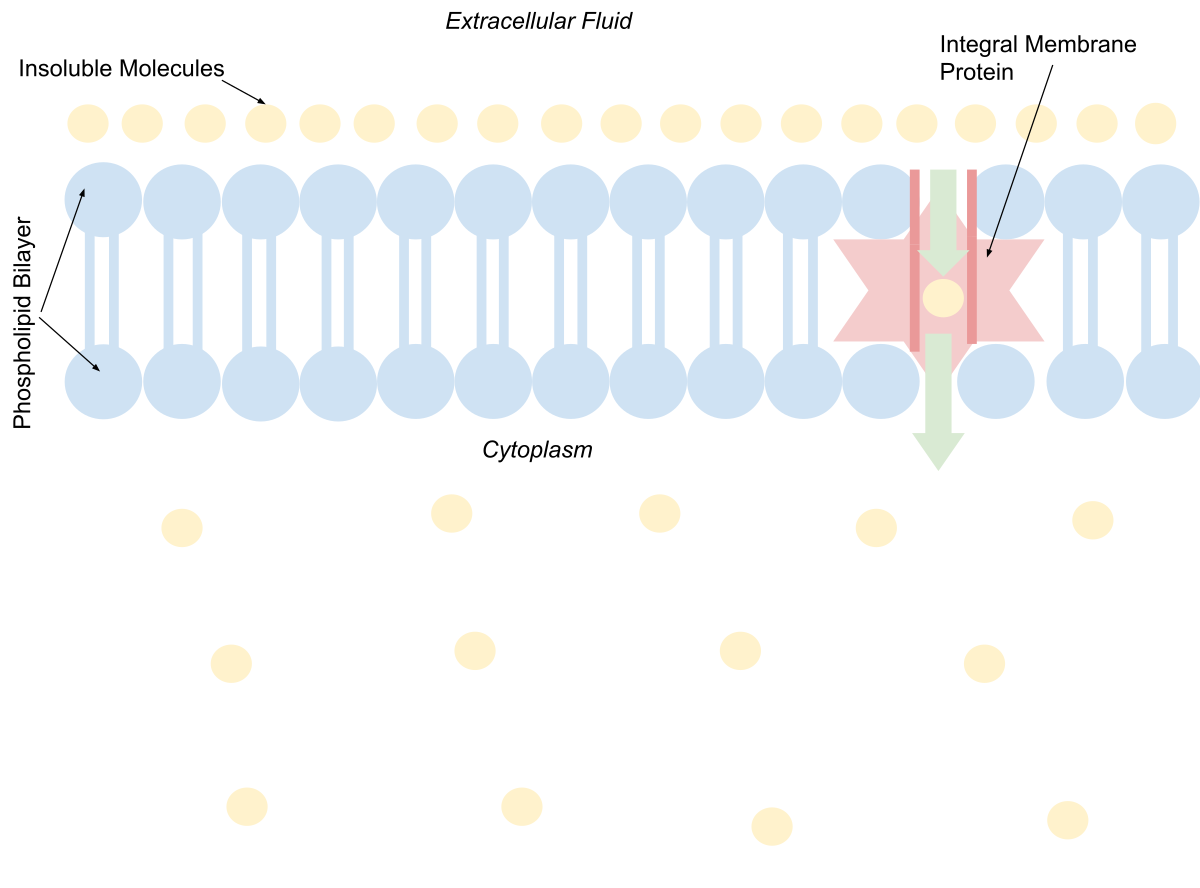 Facilitated Diffusion Wikipedia
Facilitated Diffusion Wikipedia
 Insulin Acts As The Key Which Unlocks The Cell To Allow Glucose
Insulin Acts As The Key Which Unlocks The Cell To Allow Glucose
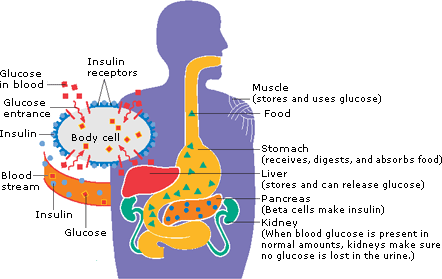 How Insulin Works With Glucose Kaiser Permanente Washington
How Insulin Works With Glucose Kaiser Permanente Washington
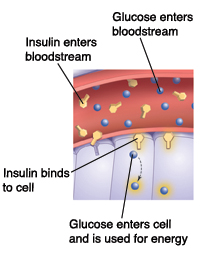
Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gcqsqfh Ryxxxadk1cvu 50p561edsfwhutpxplkrkf7skmrugmx Usqp Cau
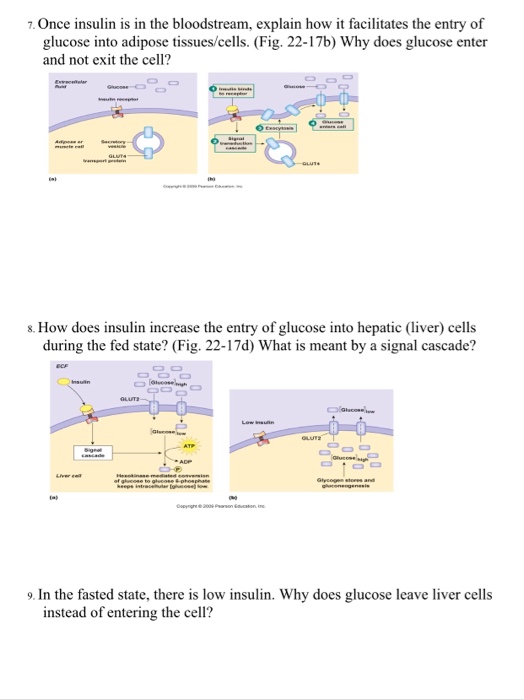
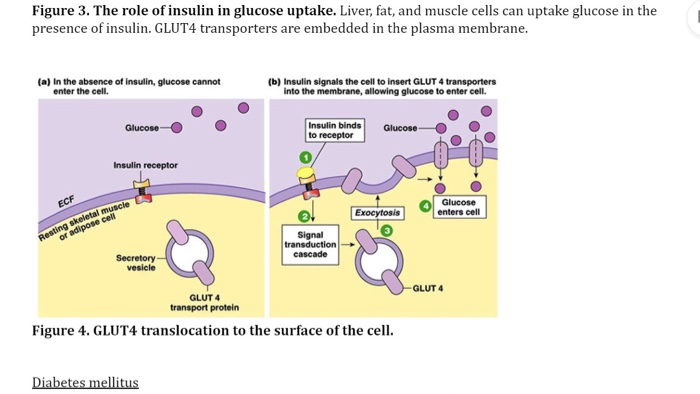 Solved Glucose Uptake After Digestion Glucose Circulates
Solved Glucose Uptake After Digestion Glucose Circulates
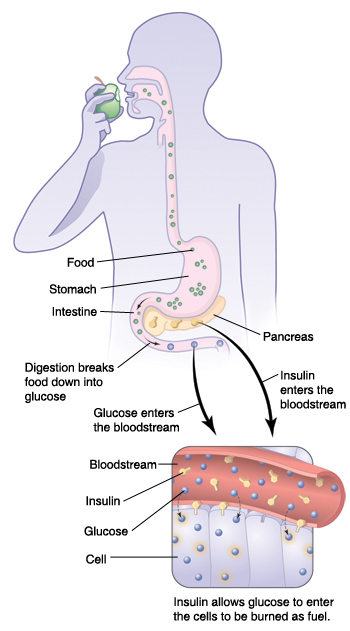
 Mechanism By Which Dietary Fat Can Raise Blood Glucose And Insulin
Mechanism By Which Dietary Fat Can Raise Blood Glucose And Insulin

 Unit 2 Med Arts Study Guide Biological Sciences 350 With Wearren
Unit 2 Med Arts Study Guide Biological Sciences 350 With Wearren
 Diabetes What Is Its Causes And What Can Be Done About It
Diabetes What Is Its Causes And What Can Be Done About It
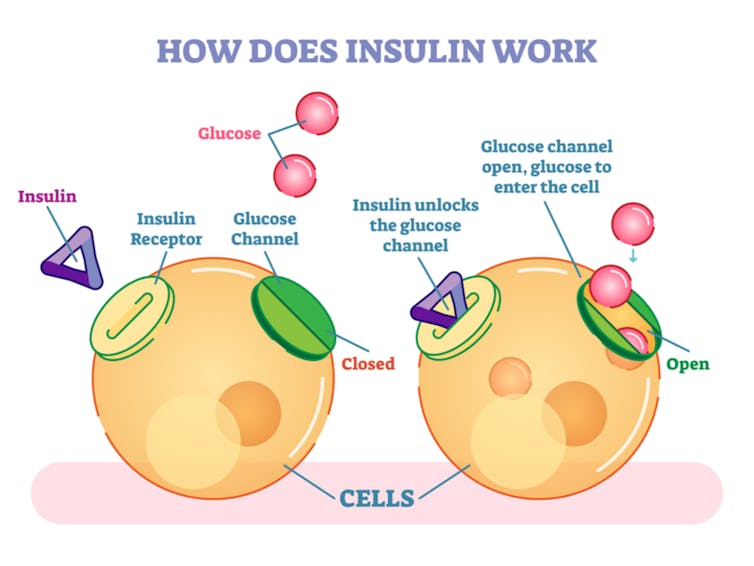 Diabetes New Test Could Detect The Disease Much Earlier
Diabetes New Test Could Detect The Disease Much Earlier
 Circulating Glucose And Lactate Enter The Cell Via Transport
Circulating Glucose And Lactate Enter The Cell Via Transport
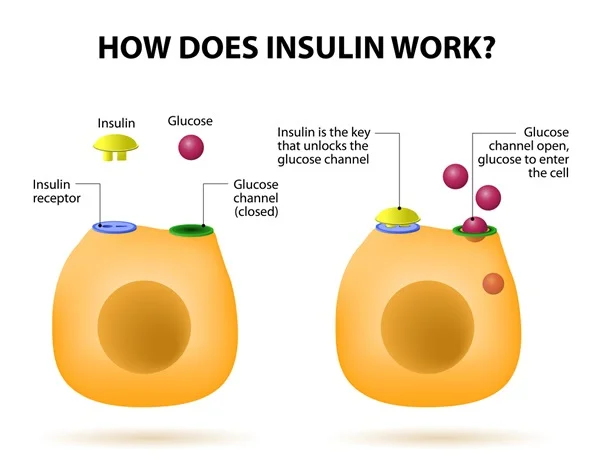 Insulin S Role In The Human Body
Insulin S Role In The Human Body
 Scheme 1 Illustrate How Blood Glucose Enter Body Cells And
Scheme 1 Illustrate How Blood Glucose Enter Body Cells And
 Insulin Acts Key Which Unlocks Cell Stock Vector Royalty Free
Insulin Acts Key Which Unlocks Cell Stock Vector Royalty Free
 Insulin Resistance And Weight Gain Weight Loss Resources
Insulin Resistance And Weight Gain Weight Loss Resources






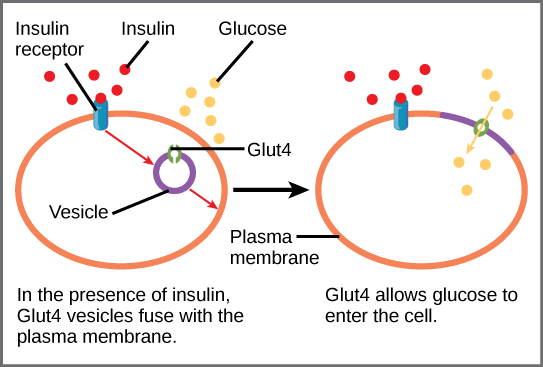


Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar