What Do Glycoproteins Do
An example is when the sugar. They can be divided in two main types.
 Glycoproteins An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Glycoproteins An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
A glycopeptide is similar in structure to a glycoprotein but has a shorter chain of amino acids.
What do glycoproteins do. The molecules are produced in abundance in the body s cells and have been under intense study for some time. Glycoproteins are proteins that have sugars attached to them. Glycoproteins depend on sugar to function properly.
In the nervous system of the rat approximately 85 90 of the brain glycoproteins include the asparagine like n glycosidic linkage bearing branched oligosaccharides. P glycosylation occurs when the sugar attaches to the phosphorus of phosphoserine. Hormones that are glycoproteins include.
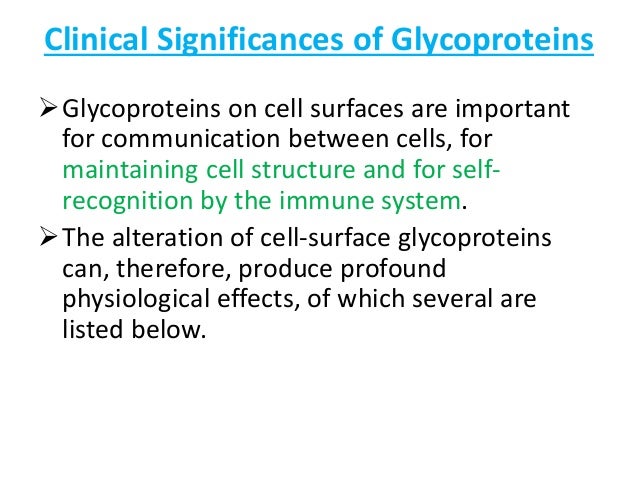
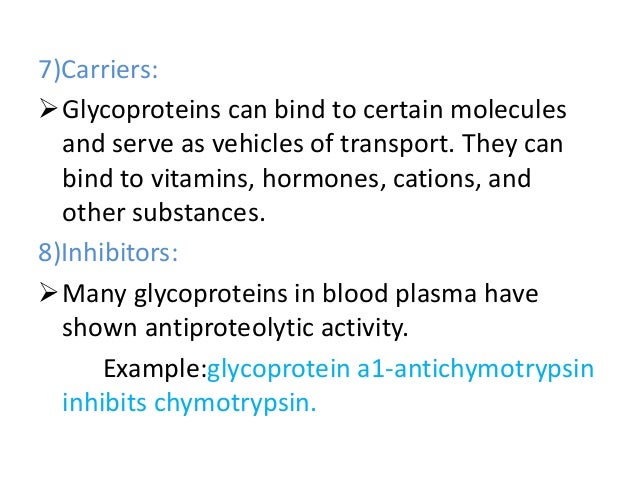
They do many important jobs for the body such as helping the immune digestive and reproductive systems. Many viruses have glycoproteins that help them. Malignant transformation a lipid membrane containing a glycoprotein that recognizes and binds to cell.
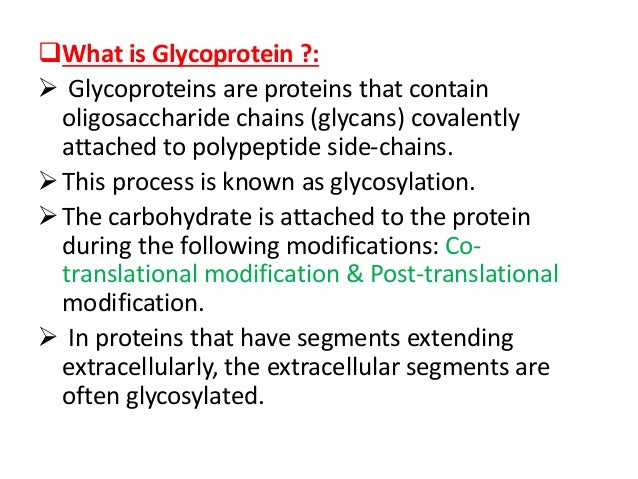
Glycoproteins are molecules that comprise of protein and carbohydrate chains that are involved in many physiological functions including immunity. N glycoproteins and o glycoproteins. C glycosylation is when the sugar attaches to the carbon atom of an amino acid.
Glycoproteins are a form of protein that contains sugar residue. Follicle stimulating hormone luteinizing hormone thyroid stimulating hormone human chorionic gonadotropin alpha fetoprotein erythropoietin epo. The lipoprotein envelope the virion membrane are integral glycoproteins which completely traverse the.
Glycoproteins serve a number of important functions in the human body including providing structural support lubrication assisting with the immune system and have a role in every other biological function studied thus far. The different characteristics of sugar may change so that it attaches itself to a characteristic of the protein. While o linked and n linked glycoproteins are the most common forms other connections are also possible.
For instance in the immune system almost all of the key molecules involved in the immune response are glycoproteins. Glycoproteins play essential roles in the body. Glycoproteins are usually found at the surface of cells and assist with important processes in the body.
Glycoproteins play a crucial role in many biological processes 1.
 Glycoprotein Function In The Cell Membrane Video Lesson
Glycoprotein Function In The Cell Membrane Video Lesson
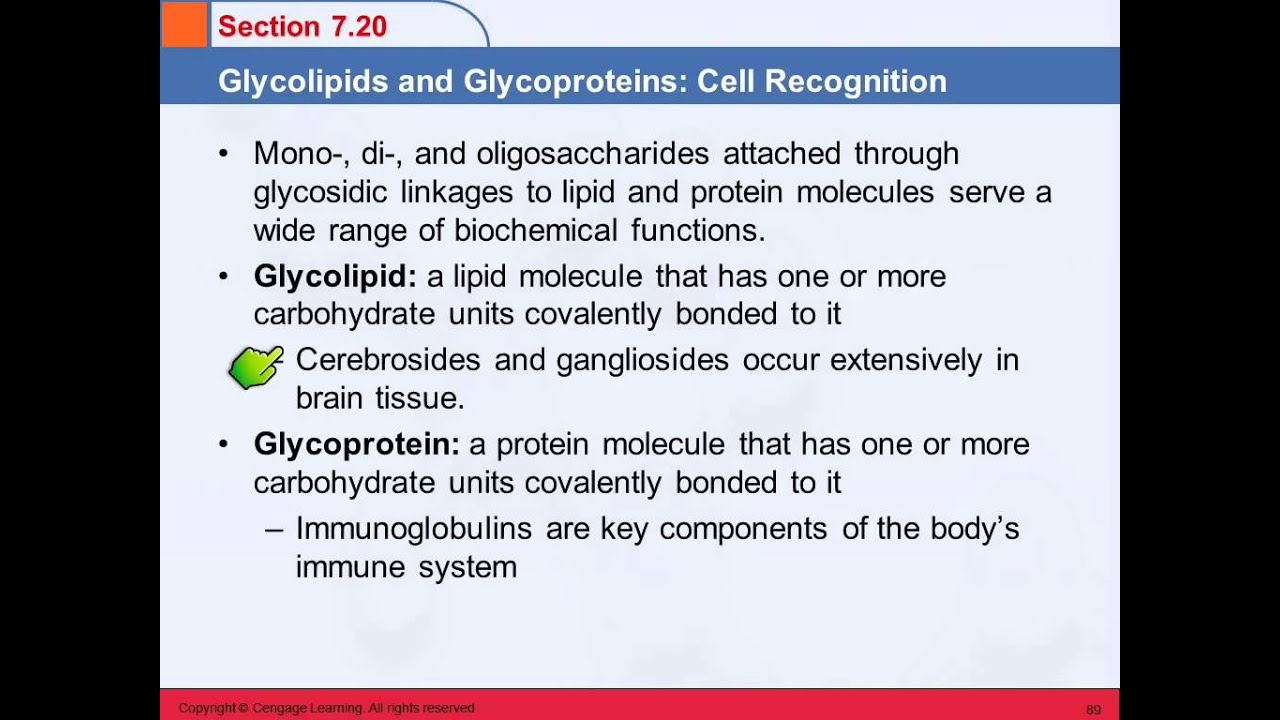 3b 7 20 Glycolipids Glycoproteins Cell Recognition Youtube
3b 7 20 Glycolipids Glycoproteins Cell Recognition Youtube
What Is The Difference Between Peptidoglycan And Glycoprotein
Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gcq0kxdawl7d5deqnkeycxdrj7xwodccmxsdjk9pldijoiod7zjh Usqp Cau
 H2 Biology Tuition H1 Biology Tuition Glycoprotein And
H2 Biology Tuition H1 Biology Tuition Glycoprotein And
What Are Glycoproteins Definition Functions Examples Video
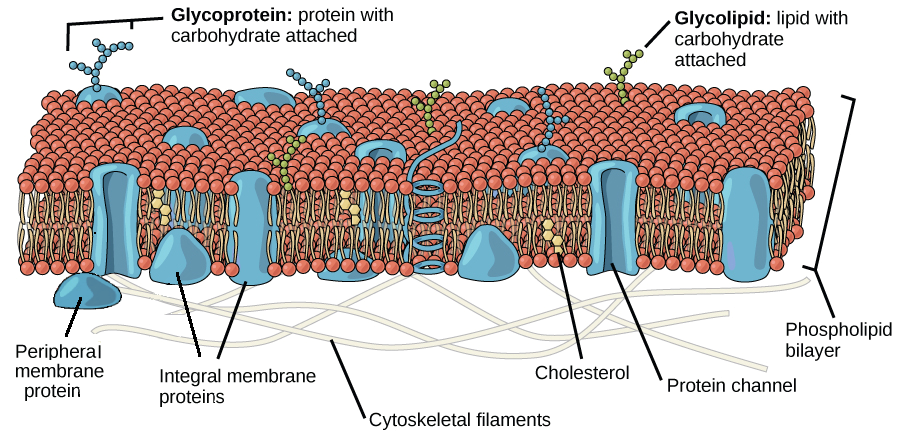 What Is The Word For Membrane Proteins That Have Carbohydrates
What Is The Word For Membrane Proteins That Have Carbohydrates
 What Are Glycoproteins Definition Functions Examples Video
What Are Glycoproteins Definition Functions Examples Video
 Glycoproteins Synthesis And Clinical Consequences
Glycoproteins Synthesis And Clinical Consequences
What Is The Difference Between Glycolipid And Glycoprotein
/antibody-1igt-562598423-58c861f35f9b58af5c557e0d.jpg) Glycoprotein Definition And Function
Glycoprotein Definition And Function
 Epithelial Hela Cells Do Not Secrete Hcv Glycoproteins A
Epithelial Hela Cells Do Not Secrete Hcv Glycoproteins A
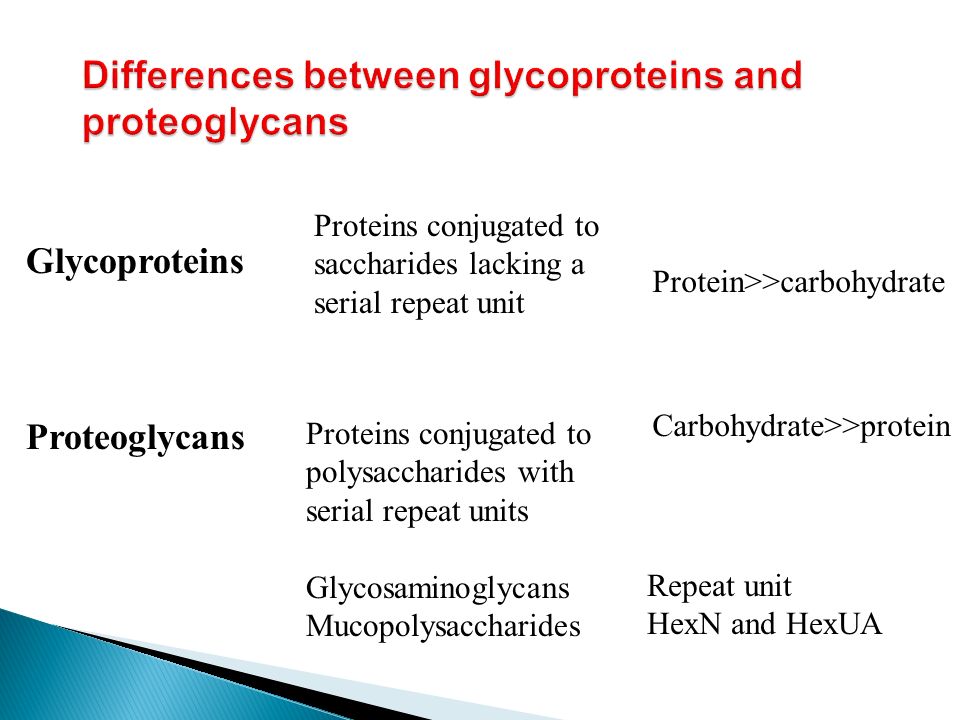 Dental Biochemistry Lecture 45 Carol Lutz Phd Complex
Dental Biochemistry Lecture 45 Carol Lutz Phd Complex
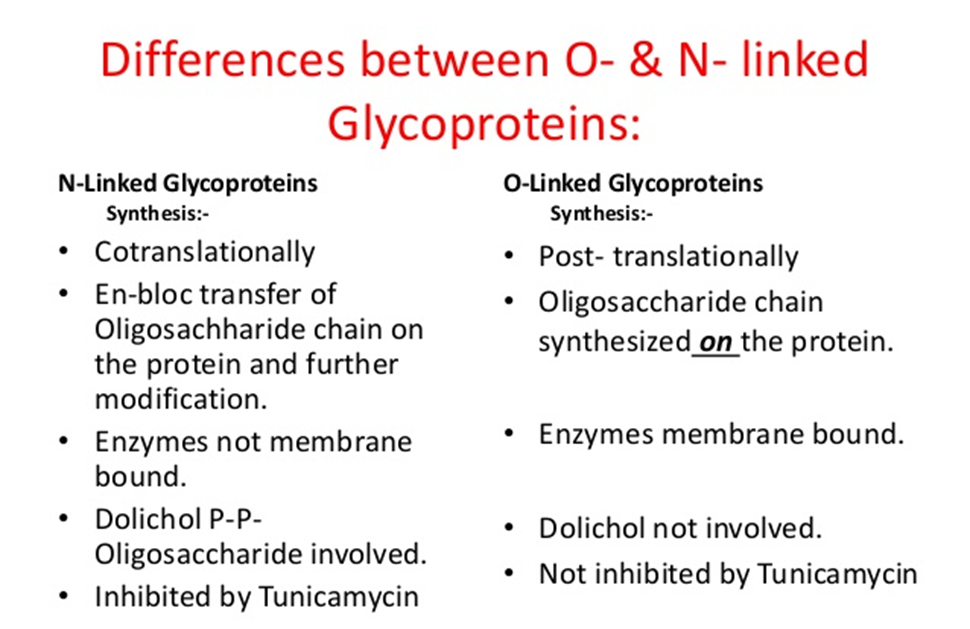
 Immunohistochemistry Scientist Cindy
Immunohistochemistry Scientist Cindy
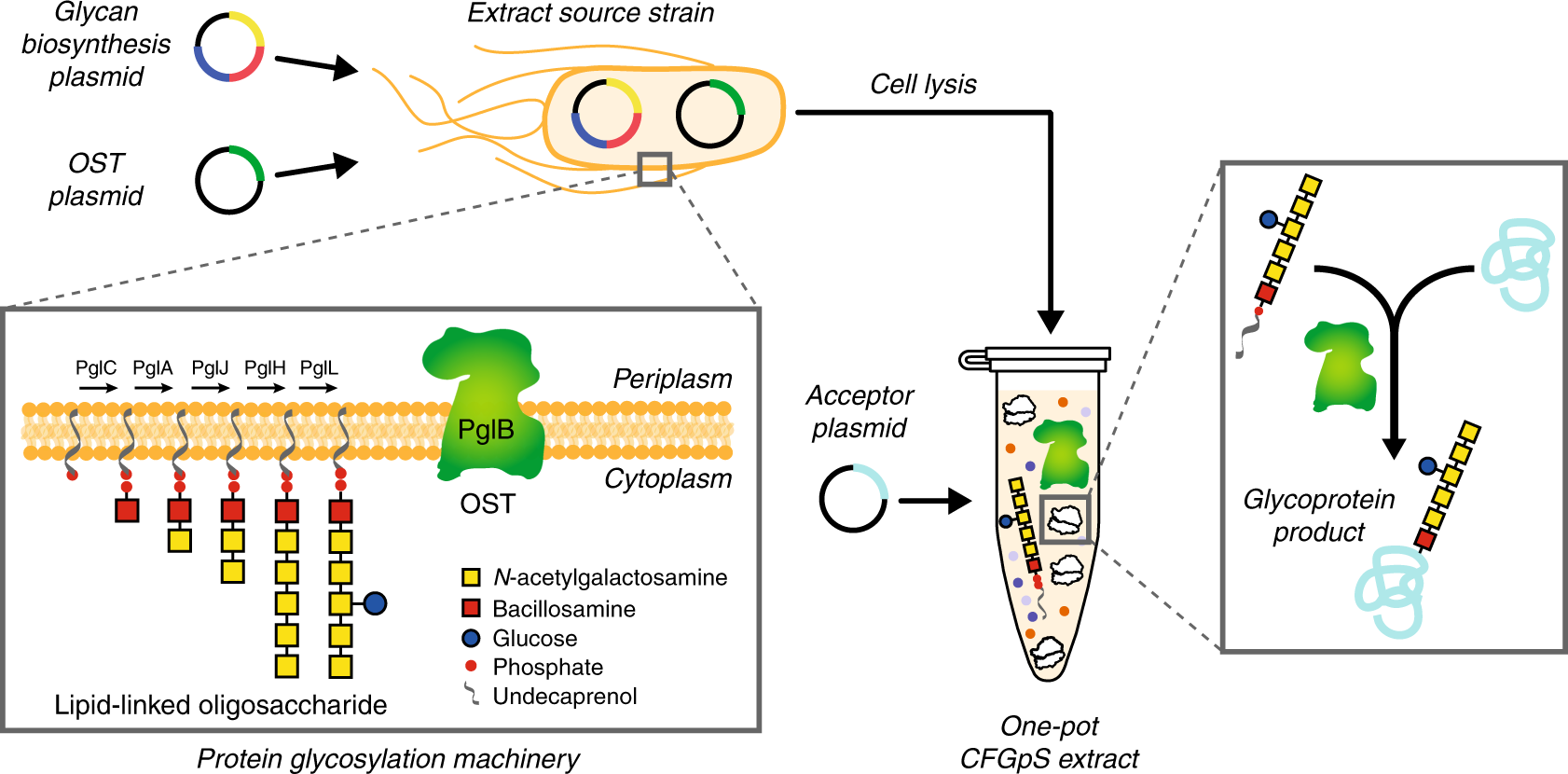 Single Pot Glycoprotein Biosynthesis Using A Cell Free
Single Pot Glycoprotein Biosynthesis Using A Cell Free
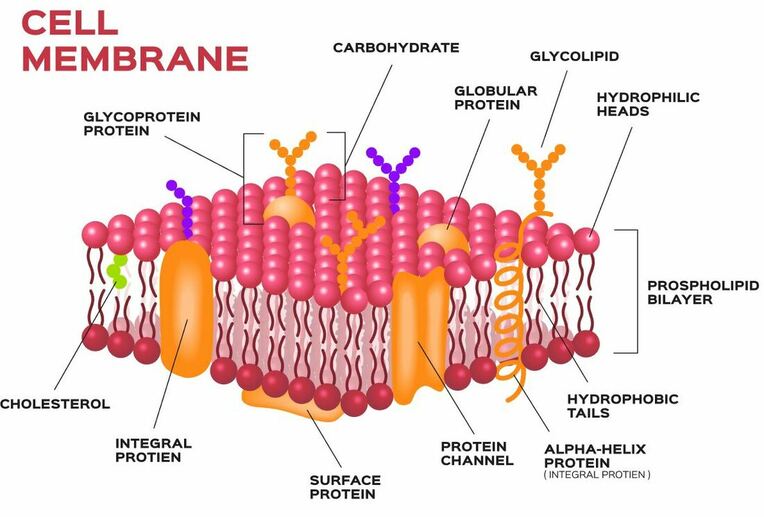
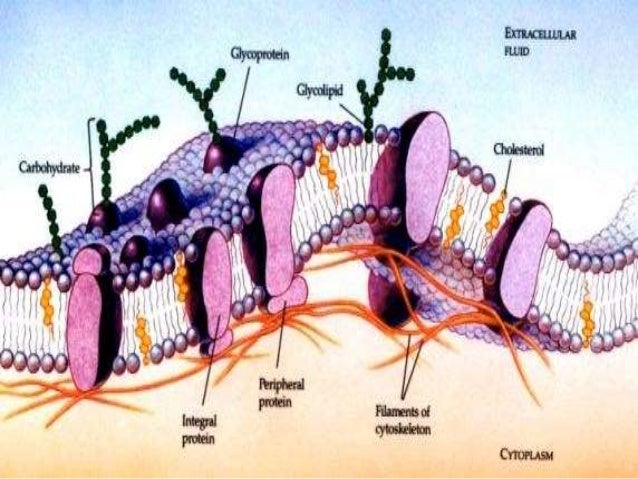
 The Cell 3 Cell Membrane Carbohydrates Atlas Of Plant And
The Cell 3 Cell Membrane Carbohydrates Atlas Of Plant And
 What Are Glycoproteins And What Do They Do By New You Health
What Are Glycoproteins And What Do They Do By New You Health
 Synthesis Of Glycoprotein Youtube
Synthesis Of Glycoprotein Youtube
 What Are Glycoproteins Definition Functions Examples Video
What Are Glycoproteins Definition Functions Examples Video
 What Are Glycoproteins And What Do They Do
What Are Glycoproteins And What Do They Do
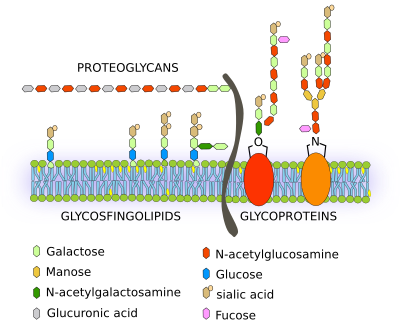
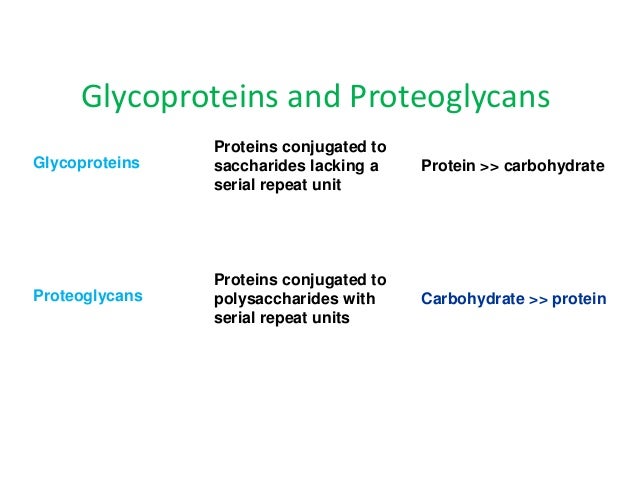
 Compare The Structures Of Proteoglycans And Glycoproteins How Are
Compare The Structures Of Proteoglycans And Glycoproteins How Are
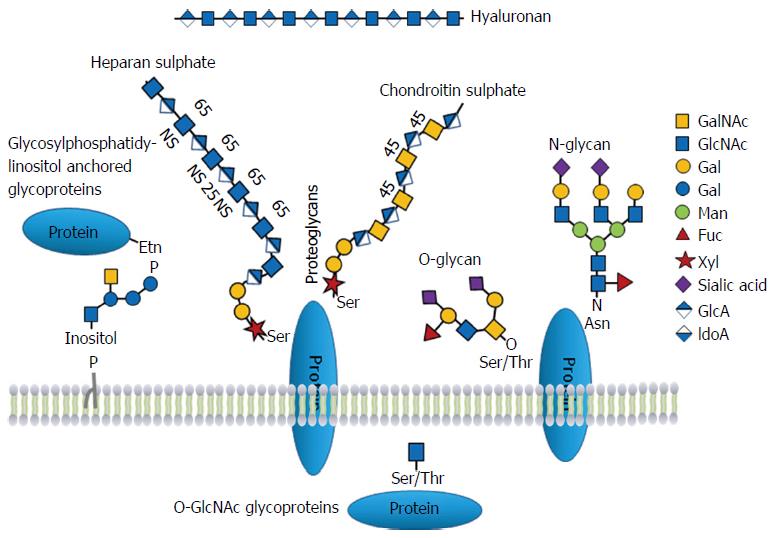 Glycoproteins And Glycoproteomics In Pancreatic Cancer
Glycoproteins And Glycoproteomics In Pancreatic Cancer
 Membrane Carbohydrate Cell Biology Microbe Notes
Membrane Carbohydrate Cell Biology Microbe Notes
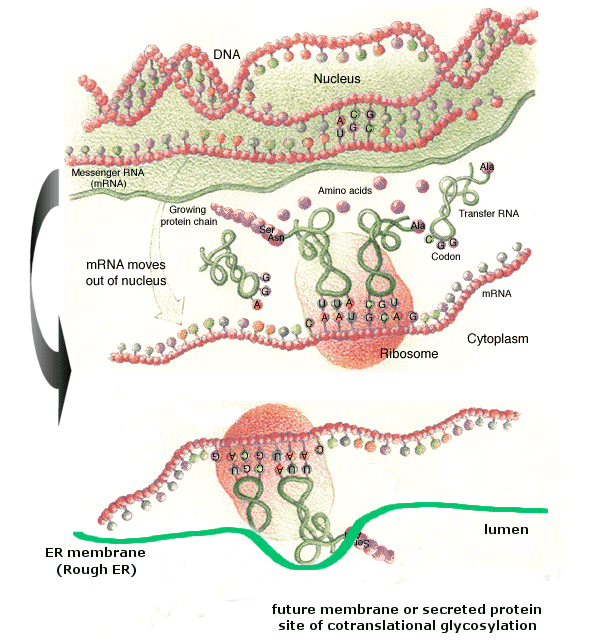

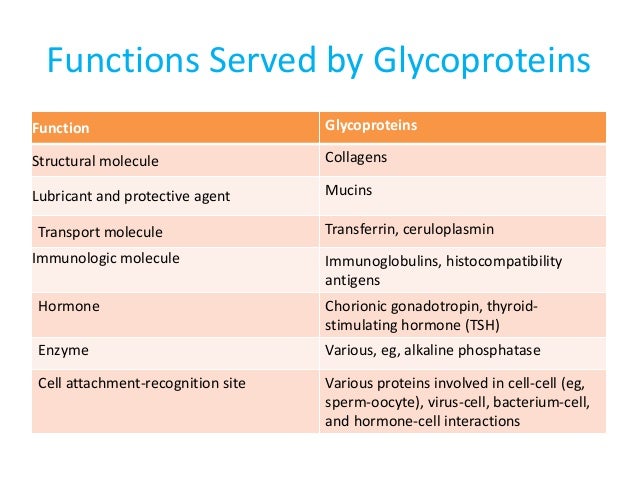



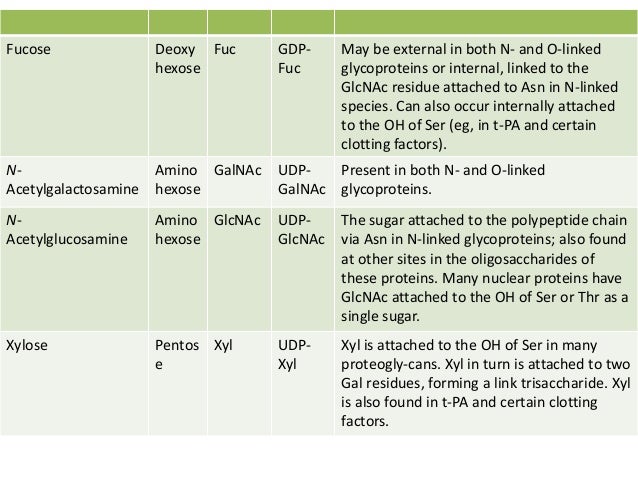
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar