Sn1 And Sn2 Reactions Primary Secondary Tertiary
Tertiary secondary primary sn2 reactions depend on the fastness of the leaving group. The hydrolysis of haloalkanes depends on the structure of the haloalkanes primary haloalkanes typically undergo s n 2 reactions whereas tertiary haloalkanes react an s n 1 mechanism for tertiary haloalkanes or tertiary alkyl halides.
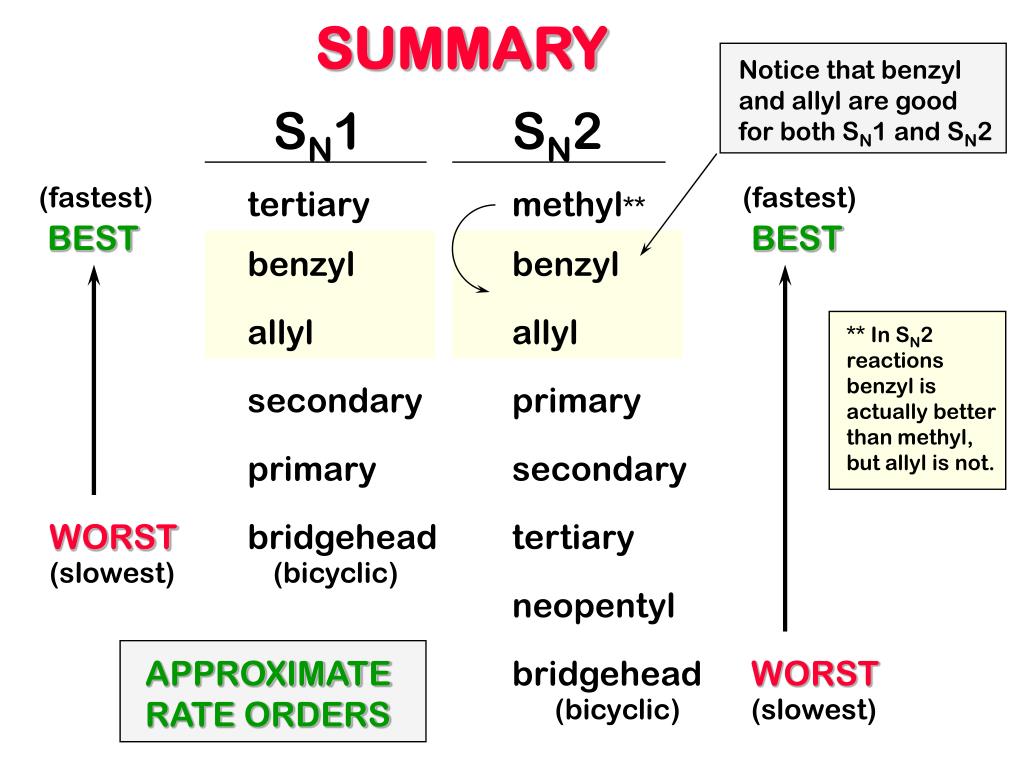 Ppt Substitution Lab Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 5068086
Ppt Substitution Lab Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 5068086
The stability of carbocation formation will determine if sn1 or sn2 reactions occur.
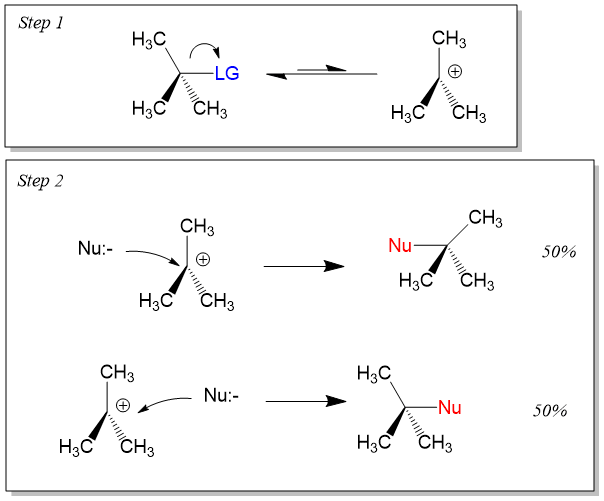
Sn1 and sn2 reactions primary secondary tertiary. Determine whether each substitution reaction shown below is likely to proceed by an s n 1 or s n 2 mechanism and explain your reasoning. On the other hand sn1 reactions are unimolecular in rate of reaction and have a step wise mechanism. 1 reactions effect of nucleophile s n 2 is a one step reaction where both the substrate and nucleophile are involved s n 1 is a two step reaction involving the initial formation of a planar carbocation therefore.
Sn1 reactions depend on the stability of the cation formed when the leaving group had left. This process first involves bond cleavage by the lg to generate a carbocation intermediate. C s n 2 b c secondary alkyl halides favor this.
B s n 1 b c tertiary alkyl halide with a weak nucleophile that is also the solvent solvolysis. Remember sn1 is where the halide comes off first and leaves behind a carbocation. For reactivity using an sn2 mechanism primary secondary tertiary carbon centers.
S n 1 nucleophile strength is unimportant s n 2 strong nucleophiles are required. Sn 1 reactions require weak nucleophiles. They are neutral solvents such as ch 3 oh h 2 o and ch 3 ch 2 oh.
So since tertiary carbocations are most stable of the three will undergo sn1 reaction easily. For sn1 the trend is the opposite the sn2 tends to proceed with strong nucleophiles. The big barrier for the sn1 is carbocation stability for sn2 the rate of reaction increases going from tertiary to secondary to primary alkyl halides.
The more stable the carbocation the higher the reactivity of the starting material. So the fastest reaction occurs in the formation of primary carbocations whereas slowest is in tertiary carbocations primary fastest secondary tertiary slowest. There are two kinds of reactions of haloalkanes naming sn1 and sn2 reaction.
A s n 2 b c primary alkyl halide with a strong nucleophile in a polar aprotic solvent.
 06 Alkyl Halides Nucleophilic Substitution And Elimination Wade
06 Alkyl Halides Nucleophilic Substitution And Elimination Wade
Substitution Reactions Of Alcohols Cssac
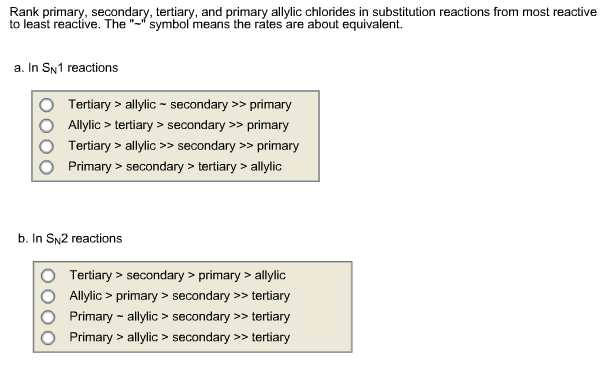 Solved Rank Primary Secondary Tertiary And Primary All Chegg Com
Solved Rank Primary Secondary Tertiary And Primary All Chegg Com
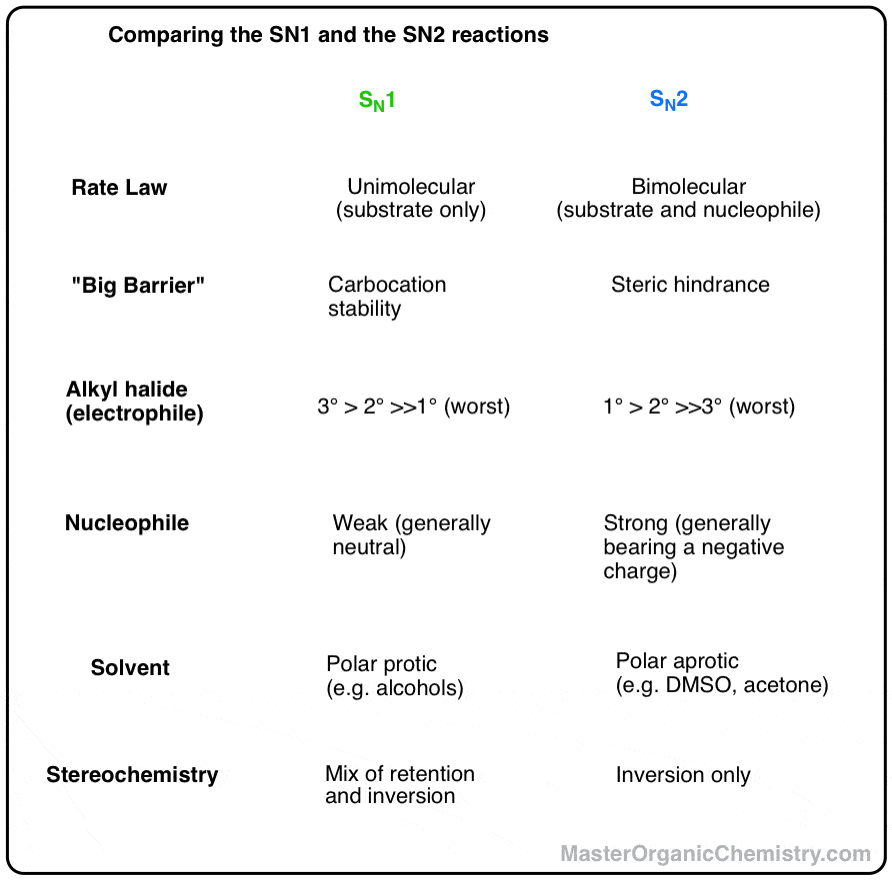 Comparing The Sn1 Vs Sn2 Reactions Master Organic Chemistry
Comparing The Sn1 Vs Sn2 Reactions Master Organic Chemistry
 Organic Chemistry I Lab School Of Science Amp Technology
Organic Chemistry I Lab School Of Science Amp Technology
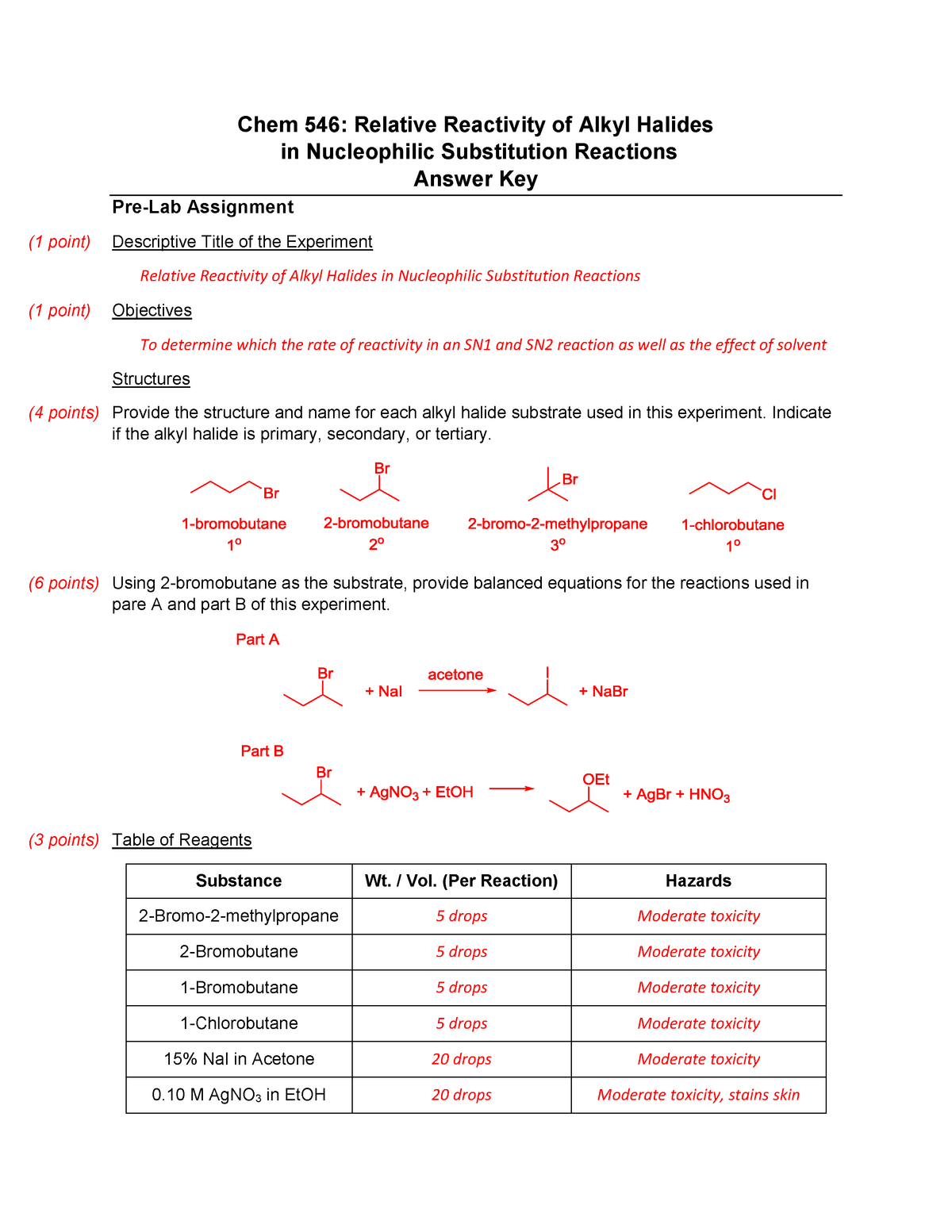 Reactivity Of Alkyl Halides Key Organic Chemistry Unh Studocu
Reactivity Of Alkyl Halides Key Organic Chemistry Unh Studocu
Https As Vanderbilt Edu Chemistry Rizzo Chem2211 Chapter7 Pdf
 When Is The Mechanism Sn1 Or Sn2 Chemistry Steps
When Is The Mechanism Sn1 Or Sn2 Chemistry Steps
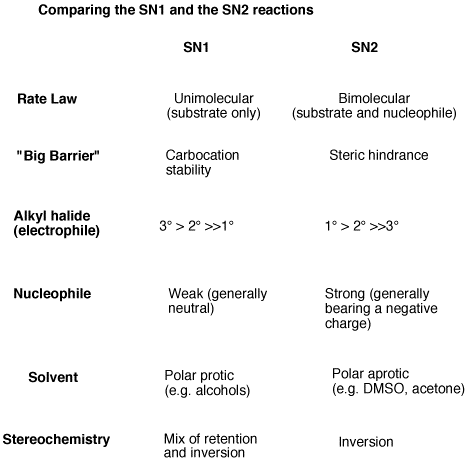 Sn1 And Sn2 Reactions Chemquestblog
Sn1 And Sn2 Reactions Chemquestblog
 When Is The Mechanism Sn1 Or Sn2 Chemistry Steps
When Is The Mechanism Sn1 Or Sn2 Chemistry Steps
 20 1 Comparison Of Sn1 And Sn2 Reactions Youtube
20 1 Comparison Of Sn1 And Sn2 Reactions Youtube
 Sn1 Sn2 E1 E2 How To Choose The Coorect Mechanism
Sn1 Sn2 E1 E2 How To Choose The Coorect Mechanism
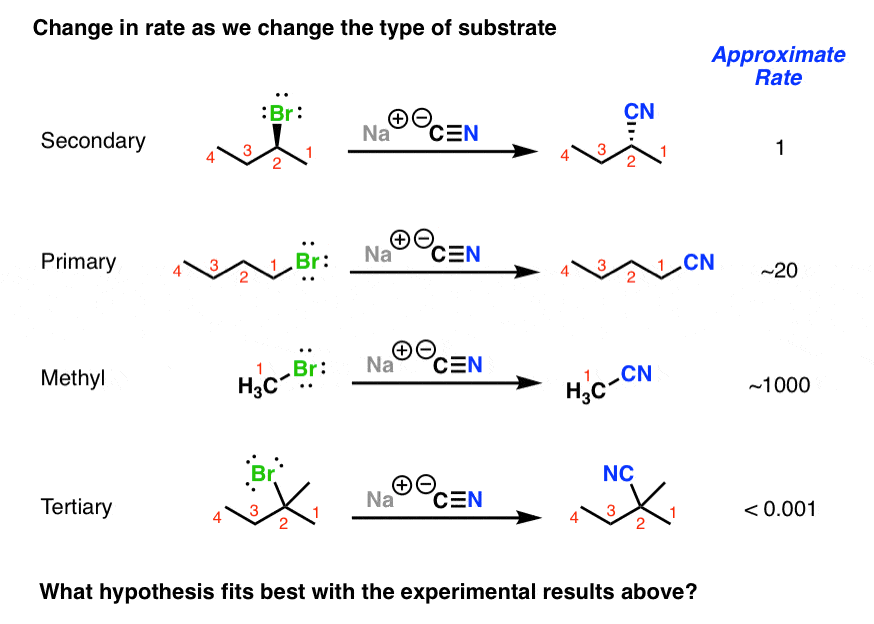 The Sn2 Reaction Mechanism Master Organic Chemistry
The Sn2 Reaction Mechanism Master Organic Chemistry
 Topic 16 Haloalkanes Chemistrycorner
Topic 16 Haloalkanes Chemistrycorner
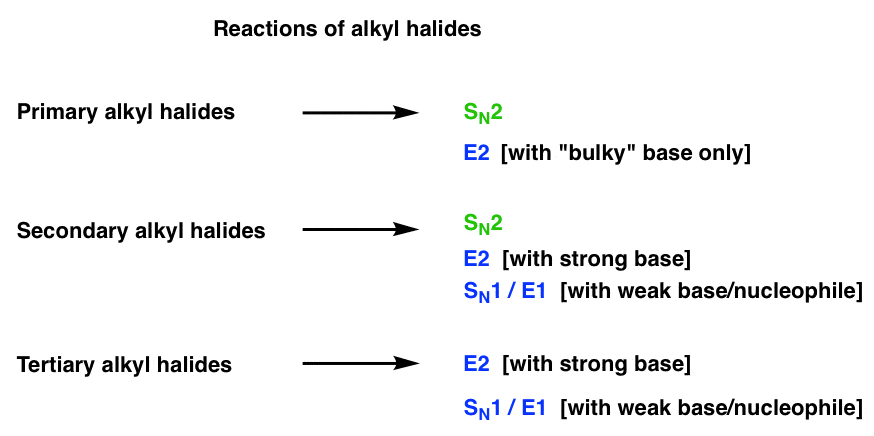 Alkyl Halide Reaction Map 14 Key Reactions Of Alkyl Halides
Alkyl Halide Reaction Map 14 Key Reactions Of Alkyl Halides
Alcohols Oxygen Containing Compounds Mcat Review
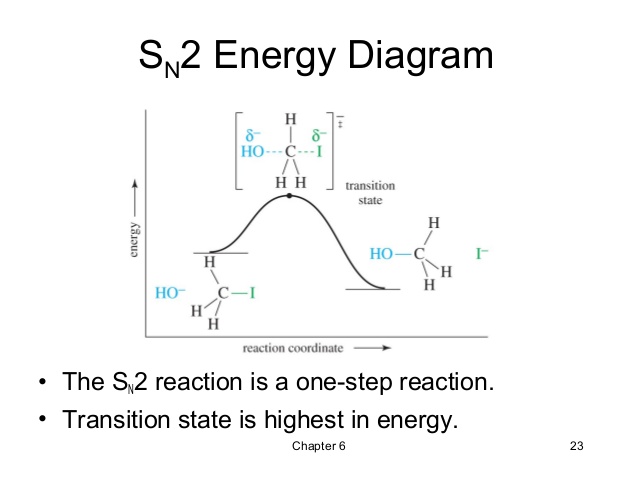 Substitution Reaction Nucleophillic Substitution Reaction Transition State
Substitution Reaction Nucleophillic Substitution Reaction Transition State
Alcohols Oxygen Containing Compounds Mcat Review
 How To Distinguish The Reaction Whether It Is Sn1 Or Sn2 Or E1 Or E2 Just By Looking At The Reaction Quora
How To Distinguish The Reaction Whether It Is Sn1 Or Sn2 Or E1 Or E2 Just By Looking At The Reaction Quora
 Sn2 Mechanism An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Sn2 Mechanism An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
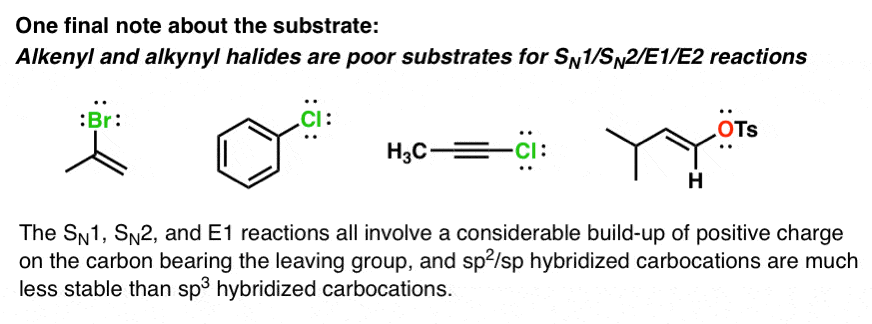 Deciding Sn1 Sn2 E1 E2 1 The Substrate Master Organic Chemistry
Deciding Sn1 Sn2 E1 E2 1 The Substrate Master Organic Chemistry
 Sn2 Mechanism An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Sn2 Mechanism An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Comparing E2 E1 Sn2 Sn1 Reactions Video Khan Academy
Comparing E2 E1 Sn2 Sn1 Reactions Video Khan Academy
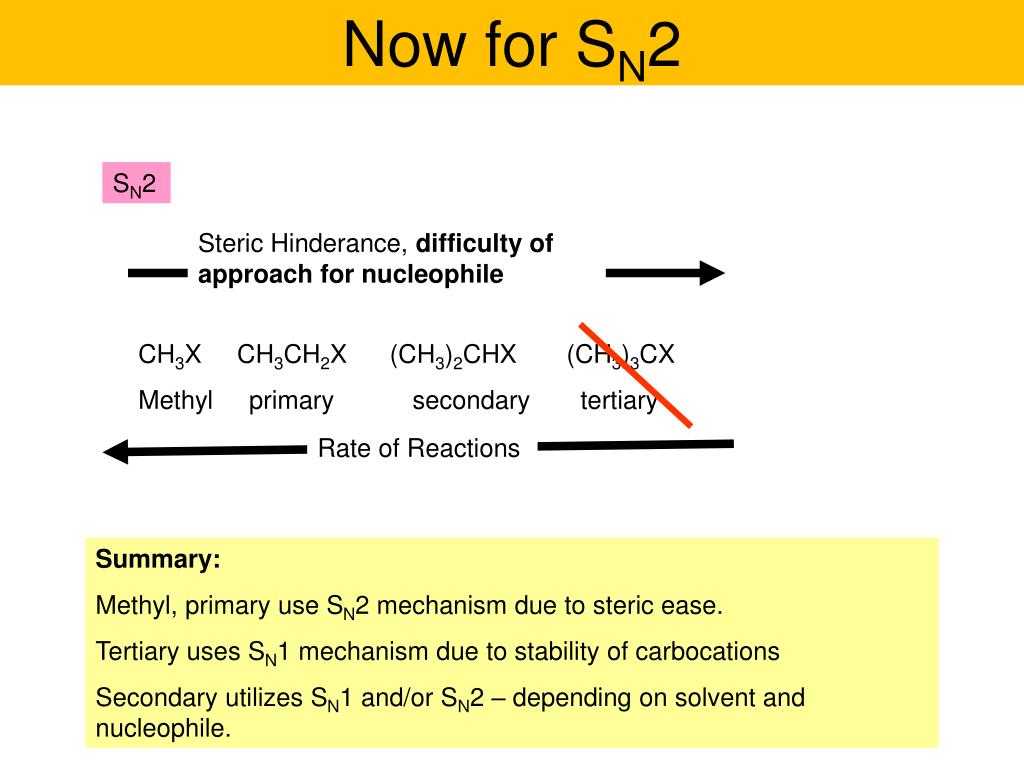 Ppt Nucleophilic Substitution And B Elimination Powerpoint Presentation Id 248704
Ppt Nucleophilic Substitution And B Elimination Powerpoint Presentation Id 248704
 When Is The Mechanism Sn1 Or Sn2 Chemistry Steps
When Is The Mechanism Sn1 Or Sn2 Chemistry Steps
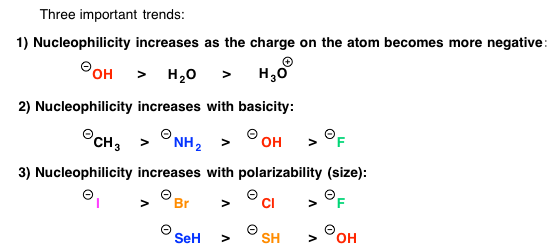 Substitution Sn2 Sn1 Reaction Organic Chemistry Help
Substitution Sn2 Sn1 Reaction Organic Chemistry Help
Why Do Primary Alkyl Halides Generally Undergo Sn2 Mechanisms Socratic
 Sn1 Or Sn2 Reaction Chemistry Stack Exchange
Sn1 Or Sn2 Reaction Chemistry Stack Exchange
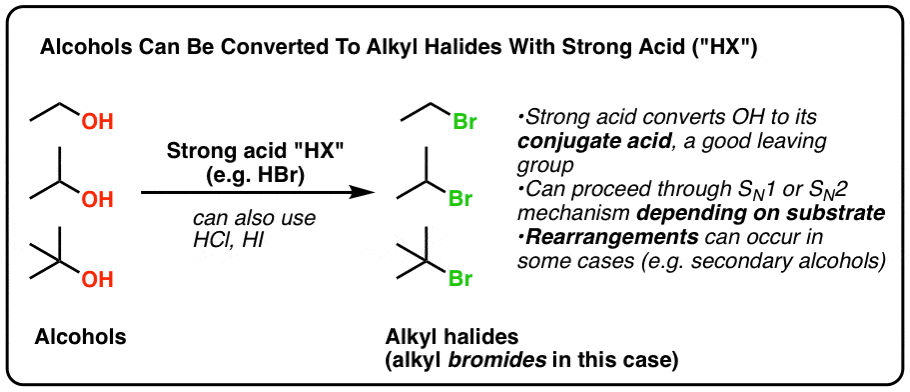 Making Alkyl Halides From Alcohols Master Organic Chemistry
Making Alkyl Halides From Alcohols Master Organic Chemistry
 Deciding Sn1 Sn2 E1 E2 1 The Substrate Organic Chemistry Study Chemistry Organic Chemistry Reactions
Deciding Sn1 Sn2 E1 E2 1 The Substrate Organic Chemistry Study Chemistry Organic Chemistry Reactions
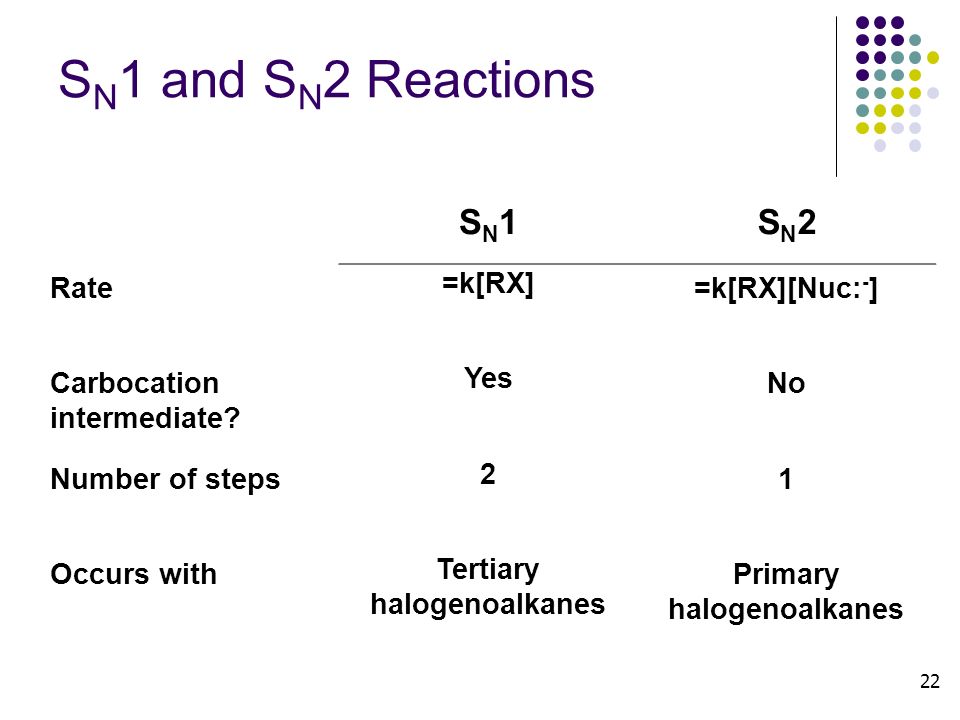 Halogenoalkanes And Reaction Pathways Ppt Video Online Download
Halogenoalkanes And Reaction Pathways Ppt Video Online Download
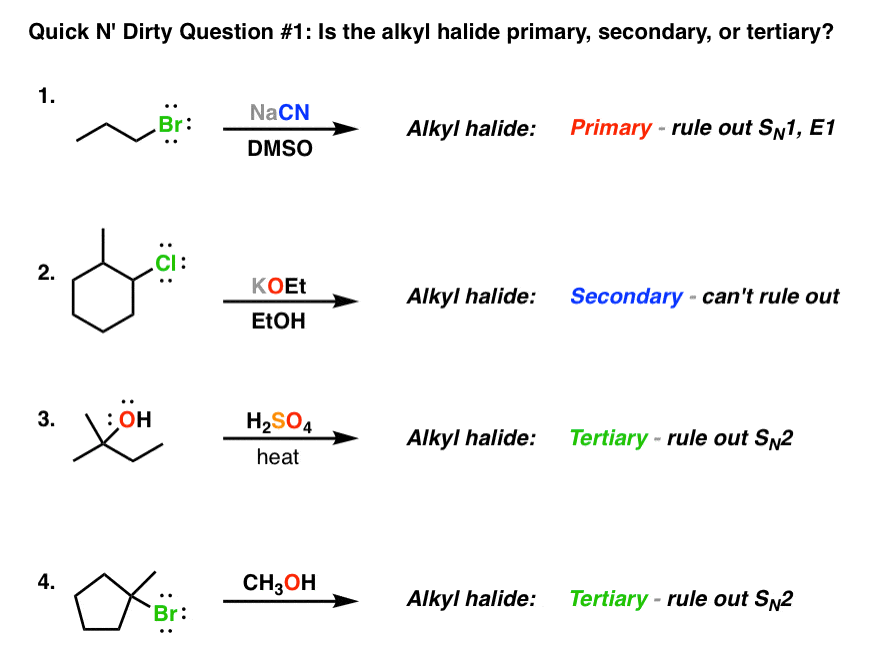 Deciding Sn1 Sn2 E1 E2 1 The Substrate Master Organic Chemistry
Deciding Sn1 Sn2 E1 E2 1 The Substrate Master Organic Chemistry
 Substitution Sn2 Sn1 Reaction Organic Chemistry Help
Substitution Sn2 Sn1 Reaction Organic Chemistry Help
Why Do Primary Alkyl Halides Generally Undergo Sn2 Mechanisms Socratic

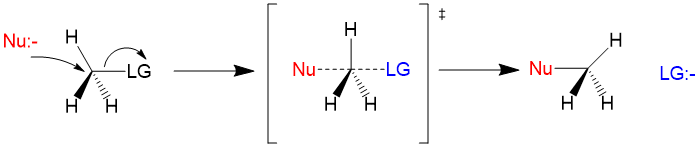 Substitution Sn2 Sn1 Reaction Organic Chemistry Help
Substitution Sn2 Sn1 Reaction Organic Chemistry Help
 Elimination Vs Substitution Secondary Substrate Video Khan Academy
Elimination Vs Substitution Secondary Substrate Video Khan Academy
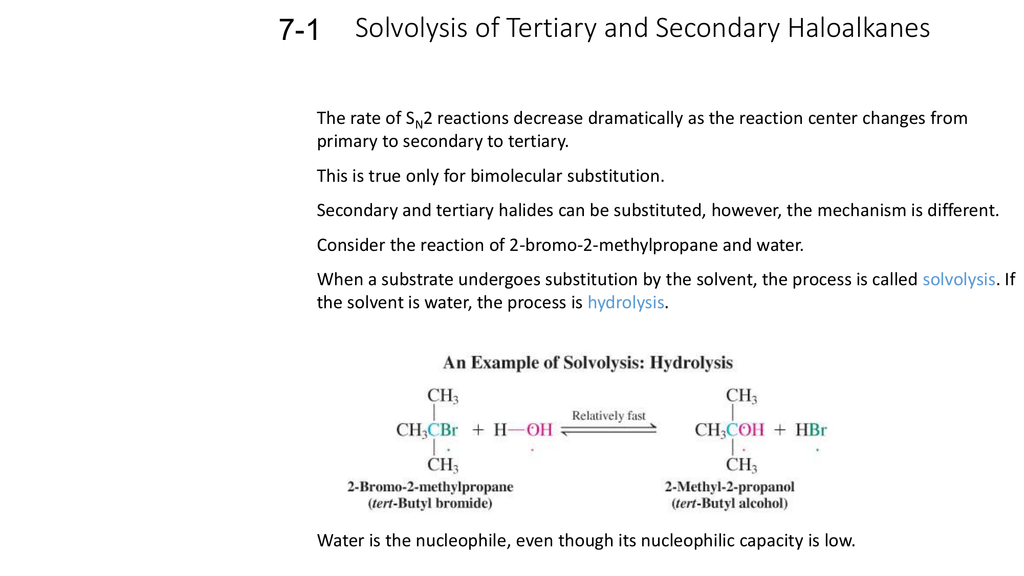
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar