Blood Plasma Vs Interstitial Fluid
Plasma can be found inside the blood vessels while interstitial fluid can be found in the tissue spaces. Interstitial fluid is the fluid that surrounds the cells of your tissue below your skin and usually glucose moves from your blood vessels and capillaries first and then into your interstitial fluid.
The interstitial fluid if is part of the extracellular fluid ecf between the cells.

Blood plasma vs interstitial fluid. The main component of the extracellular fluid ecf is the interstitial fluid or tissue fluid which surrounds the cells in the body. Materials travel between cells and the plasma in capillaries through the if. There is a 3 5 mg ml difference between arterial and venous levels with higher differences in the postprandial state.
The extracellular fluid found within the vascular system is the blood plasma. The key difference between plasma and interstitial fluid is that the plasma lies within the blood vessels and it is the liquid portion of the blood while the interstitial fluid lies between the cells of the tissues. There is a 5 to 10 minute delay in isf glucose response to changes in blood glucose.
The remaining small percentage of ecf includes the transcellular fluid. Plasma contains a higher concentration of oxygen and proteins. Another difference between plasma and interstitial fluid is the protein concentration.
It s helpful to think about it like a rollercoaster where the front car is the blood glucose bg and the car in the back is the sensor glucose. Other dissolved components are also similar in both plasma and the interstitial fluid. Blood plasma is the second part of the ecf.
Not all blood glucose is created equal. Blood plasma and interstitial fluid are the major compartments of extracellular fluid. Both plasma and interstitial fluid are mainly composed of water.
However the concentration of dissolved oxygen is higher in plasma than in interstitial fluid because the cells take up and use the oxygen from the interstitial fluid during energy production. The intracellular fluid icf is the fluid within cells. Plasma is a type of extracellular fluid ecf meaning it is a body fluid found outside of rather than within cells.
The other major component of the ecf is the intravascular fluid of the circulatory system called blood plasma. B lood glucose is generally measured as the venous plasma level. Plasma and inter stitital fluid the type of extracellular fluid that bathes the outside of cells have similar concentrations of most dissolved products nutrients and electrolytes.
1 levels are higher in the arterial blood because some of the glucose diffuses from the plasma to interstitial fluid if as blood circulates through the capillary system. Intracellular fluid can be found within the cells of the body. That s the interstitial fluid isf a thin layer of fluid that surrounds the cells of the tissues below your skin not from your blood.
Finger prick blood glucose readings and sensor glucose reading won t always match and in fact are likely to be different 3. The extracellular fluid can be found outside of the cells.
 Body Fluids And Fluid Compartments Anatomy And Physiology Ii
Body Fluids And Fluid Compartments Anatomy And Physiology Ii
 Intracellular Fluid Biochemistry Britannica
Intracellular Fluid Biochemistry Britannica
 Interstitial Fluid Cycle And Its Relationship With Cancer Steemit
Interstitial Fluid Cycle And Its Relationship With Cancer Steemit
Renal Physiology Fluid Compartments Usmle Rx 2017 Renal
 Interstitial Fluid Isf The Internal Sea
Interstitial Fluid Isf The Internal Sea
 Interstitial Fluid Definition Pressure Composition Video
Interstitial Fluid Definition Pressure Composition Video
 Fluid Shifts Of Plasma To Interstitial Fluid Osmotic Pressure
Fluid Shifts Of Plasma To Interstitial Fluid Osmotic Pressure
 Lymphatic System Plasma Vs Interstitial Fluid Vs Lymph Ppt
Lymphatic System Plasma Vs Interstitial Fluid Vs Lymph Ppt
 Physiology Illustration Three Major Body Fluid Compartments
Physiology Illustration Three Major Body Fluid Compartments
 Blood Plasma Lymph And Interstitial Fluid Flows Explained Youtube
Blood Plasma Lymph And Interstitial Fluid Flows Explained Youtube
 Ionic Composition Of Blood Plasma Interstitial Fluid And
Ionic Composition Of Blood Plasma Interstitial Fluid And
Difference Between Plasma And Interstitial Fluid Definition
 Interstitial Fluid Isf The Internal Sea
Interstitial Fluid Isf The Internal Sea
 Physiology Figure Body Fluid Compartments Of A 70 Kg Adult Man
Physiology Figure Body Fluid Compartments Of A 70 Kg Adult Man
 Tissues 5 Fluid Compartments Flashcards Quizlet
Tissues 5 Fluid Compartments Flashcards Quizlet
 Distribution Of Blood Lymph And Interstitial Fluid In Human
Distribution Of Blood Lymph And Interstitial Fluid In Human
 Interstitial Fluid Phorever Young Blog
Interstitial Fluid Phorever Young Blog
What Is The Difference Between Blood Plasma And Lymph Quora
Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gct2fcci5b1wjatk2q0rcmjurh1 D1cistxgrk Thte Ro49c Ih Usqp Cau
 25 2b Fluid Compartments Medicine Libretexts
25 2b Fluid Compartments Medicine Libretexts
Fluid And Electrolyte Balance Structure And Function Nursing
Relationship Between Tissue Fluid And Lymph Definition
 Interstitial Fluid Isf The Internal Sea
Interstitial Fluid Isf The Internal Sea
 Interstitial Fluid Formation And Oedema By Dr Qazi Imtiaz Rasool
Interstitial Fluid Formation And Oedema By Dr Qazi Imtiaz Rasool
 Body Fluids And Fluid Compartments Anatomy And Physiology Ii
Body Fluids And Fluid Compartments Anatomy And Physiology Ii
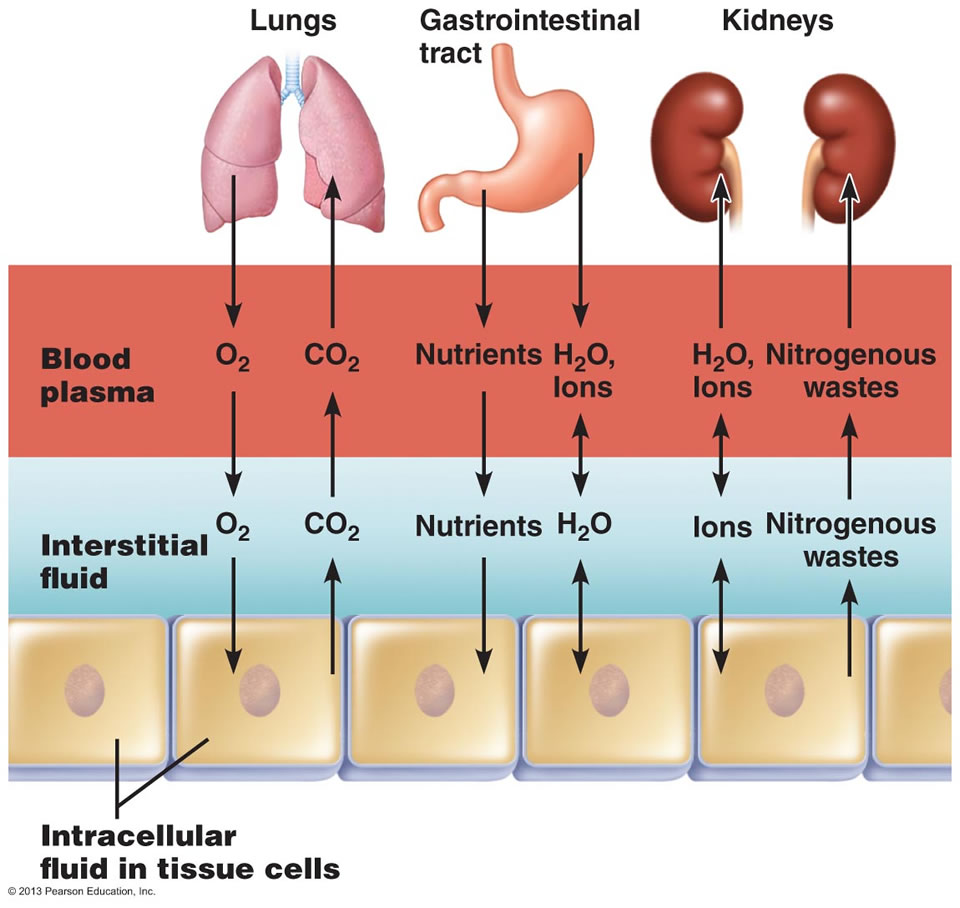 Body Fluids Anatomy Physiology
Body Fluids Anatomy Physiology
 Body Fluids Renal Physiology Physiology 5th Ed
Body Fluids Renal Physiology Physiology 5th Ed
 Body Fluids And Fluid Compartments Anatomy And Physiology Ii
Body Fluids And Fluid Compartments Anatomy And Physiology Ii
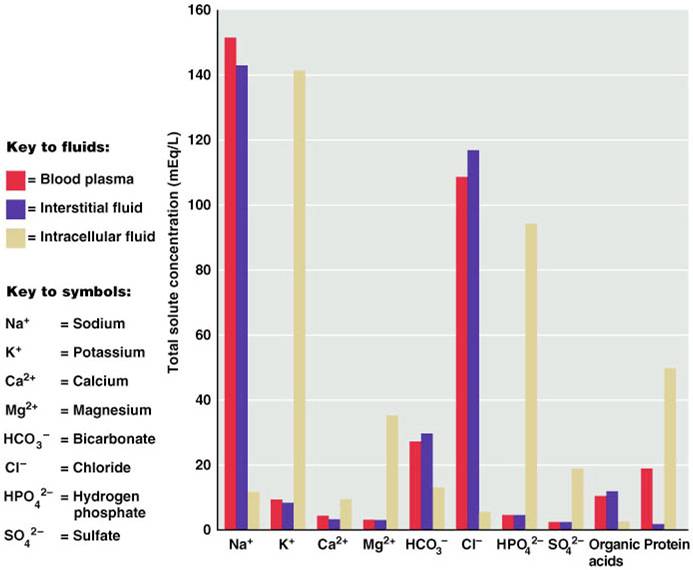 Body Fluids Anatomy Physiology
Body Fluids Anatomy Physiology
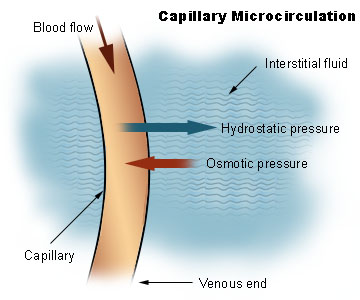 Difference Between Plasma And Interstitial Fluid Compare The
Difference Between Plasma And Interstitial Fluid Compare The
 Chapter 25 Body Fluid Compartments Dr Marko Ljubkovic Department
Chapter 25 Body Fluid Compartments Dr Marko Ljubkovic Department
 Difference Between Plasma And Interstitial Fluid Compare The
Difference Between Plasma And Interstitial Fluid Compare The
.png) Interstitial Fluid Vs Blood Glucose Freestyle Glucose Meters
Interstitial Fluid Vs Blood Glucose Freestyle Glucose Meters
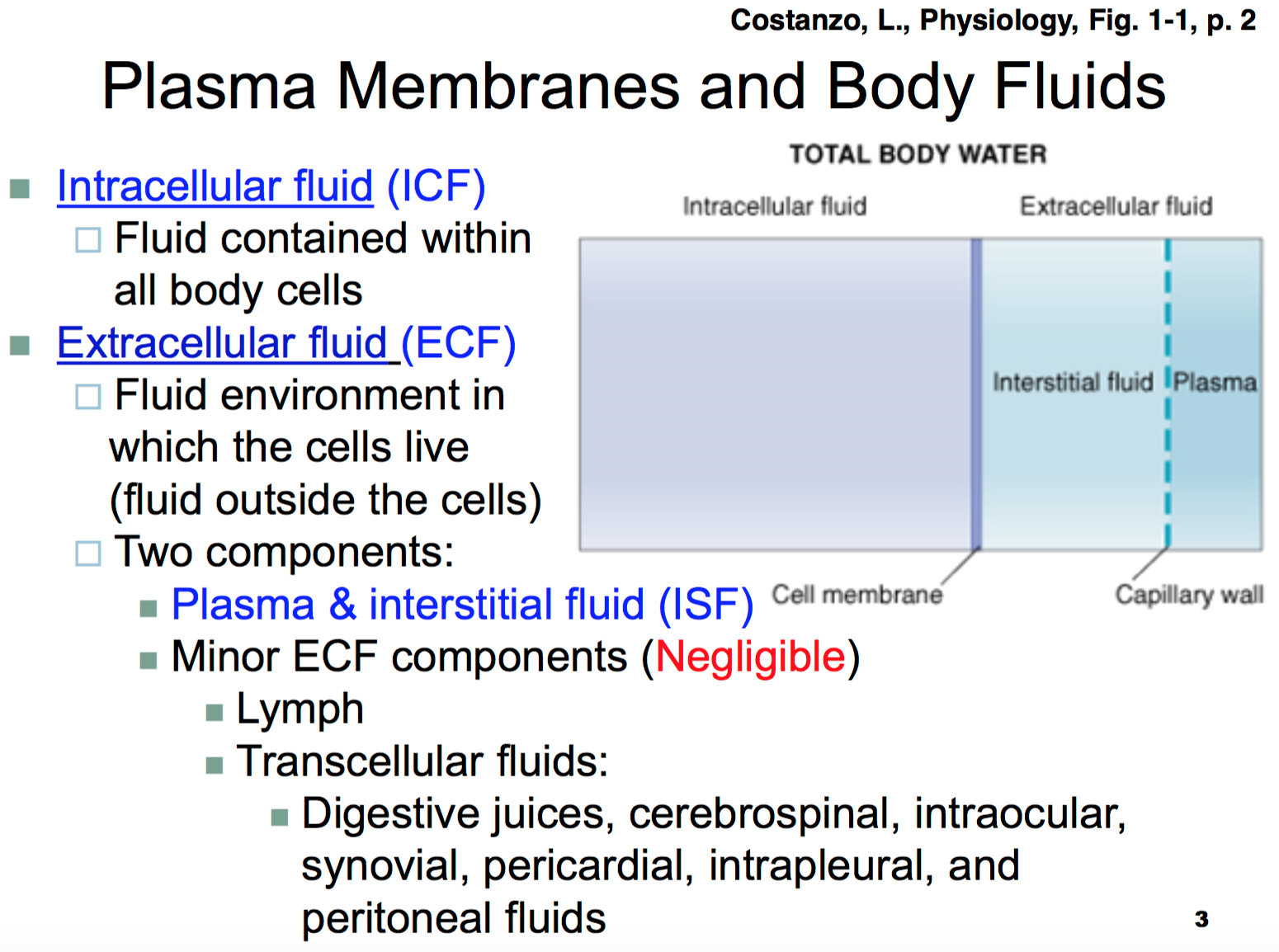






Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar